SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Immune escape and vaccine development
- PMID: 35317190
- PMCID: PMC8925644
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.126
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Immune escape and vaccine development
Abstract
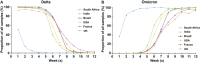
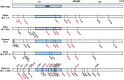
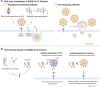
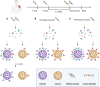
New genetic variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) constantly emerge through unmitigated spread of the virus in the ongoing Coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Omicron (B.1.1.529), the latest variant of concern (VOC), has so far shown exceptional spread and infectivity and has established itself as the dominant variant in recent months. The SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein is a key component for the recognition and binding to host cell angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptors. The Omicron variant harbors a cluster of substitutions/deletions/insertions, and more than 30 mutations are located in spike. Some noticeable mutations, including K417N, T478K, N501Y, and P681H, are shared with the previous VOCs Alpha, Beta, Gamma, or Delta variants and have been proven to be associated with higher transmissibility, viral infectivity, and immune evasion potential. Studies have revealed that the Omicron variant is partially resistant to the neutralizing activity of therapeutic antibodies and convalescent sera, which poses significant challenges for the clinical effectiveness of the current vaccines and therapeutic antibodies. We provide a comprehensive analysis and summary of the epidemiology and immune escape mechanisms of the Omicron variant. We also suggest some therapeutic strategies against the Omicron variant. This review, therefore, aims to provide information for further research efforts to prevent and contain the impact of new VOCs during the ongoing pandemic.
Keywords: Omicron variant; immune escape; spike; vaccine development.
© 2022 The Authors. MedComm published by Sichuan International Medical Exchange & Promotion Association (SCIMEA) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Kang Zhang is an editorial board member of MedComm. Author Kang Zhang was not involved in the journal's review of, or decisions related to, this manuscript. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Duffy S, Shackelton LA, Holmes EC. Rates of evolutionary change in viruses: patterns and determinants. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9(4):267‐276. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Tracking SARS‐CoV‐2 variants. 2022. Accessed February 28, 2022. https://www.who.int/activities/tracking‐SARS‐CoV‐2‐variants/tracking‐SAR...
-
- Cascella M, Rajnik M, Aleem A, Dulebohn SC, Di Napoli R. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID‐19) . StatPearls Publishing; 2022. - PubMed
-
- CoVariants . Variant: 21K (Omicron). 2022. Accessed February 28, 2022. https://covariants.org/variants/21K.Omicron
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
