Single-Cell Sequencing Revealed Pivotal Genes Related to Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction Patients
- PMID: 35317194
- PMCID: PMC8934393
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6534126
Single-Cell Sequencing Revealed Pivotal Genes Related to Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction Patients
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Single-Cell Sequencing Revealed Pivotal Genes Related to Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction Patients.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 13;2023:9895238. doi: 10.1155/2023/9895238. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 38124937 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: Myocardial infarction (MI) is a common cardiovascular disease. Histopathology is a main molecular characteristic of MI, but often, differences between various cell subsets have been neglected. Under this premise, MI-related molecular biomarkers were screened using single-cell sequencing.
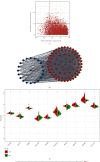
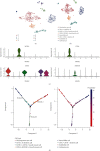
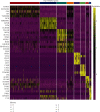
Methods: This work examined immune cell abundance in normal and MI samples from GSE109048 and determined differences in the activated mast cells and activated CD4 memory T cells, resting mast cells. Weighted gene coexpression network analysis (WGCNA) demonstrated that activated CD4 memory T cells were the most closely related to the turquoise module, and 10 hub genes were screened. Single-cell sequencing data (scRNA-seq) of MI were examined. We used t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) for cell clustering.
Results: We obtained 8 cell subpopulations, each of which had different marker genes. 7 out of the 10 hub genes were detected by single-cell sequencing analysis. The expression quantity and proportion of the 7 genes were different in 8 cell clusters.
Conclusion: In general, our study revealed the immune characteristics and determined 7 prognostic markers for MI at the single-cell level, providing a new understanding of the molecular characteristics and mechanism of MI.
Copyright © 2022 Jiamin Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

