Role of the nuclear receptor subfamily 4a in mast cells in the development of irritable bowel syndrome
- PMID: 35317226
- PMCID: PMC8907967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.02.017
Role of the nuclear receptor subfamily 4a in mast cells in the development of irritable bowel syndrome
Abstract
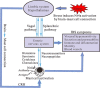
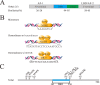
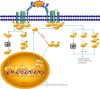
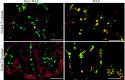
The activation of mast cells (MCs) and mediator release are closely related to the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). However, the exact underlying mechanisms are still not completely understood. The nuclear receptor subfamily 4a (Nr4a) is a family of orphan nuclear receptors implicated in regulating MC activation, degranulation, cytokine/chemokine synthesis and release. Acute and chronic stress trigger hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis (HPA) activation to induce the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), resulting in MC activation and induction of the Nr4a family. Our newest data showed that Nr4a members were specially over-expressed in colonic MCs of the chronic water-avoidance stress (WAS)-induced visceral hyperalgesia mice, suggesting that Nr4a members might be involved in the pathophysiology of visceral hypersensitivity. In this review, we highlight the present knowledge on roles of Nr4a members in the activation of MCs and the pathophysiology of IBS, and discuss signaling pathways that modulate the activation of Nr4a family members. We propose that a better understanding of Nr4a members and their modulators may facilitate the development of more selective and effective therapies to treat IBS patients.
Keywords: AF-1, activation function-1; AP-1, activator protein 1; BMMCs, bone marrow-derived MCs; CGRP, calcitonin gene-related peptide; CRH-R, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) receptor; CoREST, corepressor for element-1-silencing transcription factor; DBD, DNA-binding domain; FcεRI, high affinity IgE receptor Fc epsilon RI; HPA, hypothalamic-pituitaryadrenal axis; Hypothalamic–pituitaryadrenal axis; IBS, irritable bowel syndrome; IKK, inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase; IL, interleukin; Irritable bowel syndrome; JNK, Jun-N-terminal kinase; LBD, ligand-binding domain; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MCs, mast cells; Mast cells; NBRE, nerve growth factor-induced clone B (NGFI-B) response element; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T-cells; NOR1, neuron-derived orphan receptor 1; Nr4a, nuclear receptor subfamily 4a; Nuclear receptor subfamily 4a; NurRE, Nur response element; P2X7, P2X purinoceptor 7; PAR2, protease--activated receptor 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; PKCα, protein kinase C alpha; RSK, ribosomal S6 kinase; RXR, retinoid X receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; WAS, chronic water-avoidance stress; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not have any conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of Nr4a subfamily nuclear receptors following mast cell activation.Mol Immunol. 2011 Sep;48(15-16):1753-61. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2011.04.017. Epub 2011 May 31. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21621845
-
Altered gene expression signatures by calcitonin gene-related peptide promoted mast cell activity in the colon of stress-induced visceral hyperalgesia mice.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Jun;33(6):e14073. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14073. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33382180
-
How glucocorticoid receptors modulate the activity of other transcription factors: a scope beyond tethering.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013 Nov 5;380(1-2):41-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.12.014. Epub 2012 Dec 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23267834 Review.
-
Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in mast cells contributes to the regulation of inflammatory cytokines in irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016 Jul;28(7):1083-93. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12811. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016. PMID: 26940641
-
Role of corticotropin-releasing hormone in irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal inflammation.J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan;42 Suppl 17:48-51. doi: 10.1007/s00535-006-1942-7. J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17238026 Review.
Cited by
-
Store-operated calcium entry mediates hyperalgesic responses during neuropathy.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Nov;13(11):2020-2034. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13699. Epub 2023 Aug 28. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37606998 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Screening Reveals De Novo Loss-of-Function NR4A2 Variants in Saudi Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders: A Single-Center Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 7;26(12):5468. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125468. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40564942 Free PMC article.
-
Neural circuits regulating visceral pain.Commun Biol. 2024 Apr 13;7(1):457. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06148-y. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38615103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Mast Cell Stabilizer JM25-1 Rehabilitates Impaired Gut Barrier by Targeting the Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;16(1):47. doi: 10.3390/ph16010047. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36678544 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
