Development of a dynamic network biomarkers method and its application for detecting the tipping point of prior disease development
- PMID: 35317238
- PMCID: PMC8907966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.02.019
Development of a dynamic network biomarkers method and its application for detecting the tipping point of prior disease development
Abstract
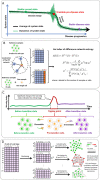
The dynamic network biomarker (DNB) method has advanced since it was first proposed. This review discusses advances in the DNB method that can identify the dynamic change in the expression signature related to the critical time point of disease progression by utilizing different kinds of transcriptome data. The DNB method is good at identifying potential biomarkers for cancer and other disease development processes that are represented by a limited molecular profile change between the normal and critical stages. We highlight that the cancer tipping point or premalignant state has been widely discovered for different types of cancer by using the DNB method that utilizes bulk or single-cell RNA sequencing data. This method could also be applied to other dynamic research studies and help identify early warning signals, such as the prediction of a pre-outbreak of COVID-19. We also discuss how the identification of reliable biomarkers of cancer and the development of new methods can be utilized for early detection and intervention and provide insights into emerging paths of the widespread biomarker candidate pool for further validation and disease/health management.
Keywords: Cancer; Complex disease; Dynamic network biomarker; Tipping point.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection for disease tipping points by landscape dynamic network biomarkers.Natl Sci Rev. 2019 Jul;6(4):775-785. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwy162. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Natl Sci Rev. 2019. PMID: 34691933 Free PMC article.
-
TPD: a web tool for tipping-point detection based on dynamic network biomarker.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Sep 20;23(5):bbac399. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac399. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36088546
-
Personalized Early-Warning Signals during Progression of Human Coronary Atherosclerosis by Landscape Dynamic Network Biomarker.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 20;11(6):676. doi: 10.3390/genes11060676. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575789 Free PMC article.
-
Network biomarkers, interaction networks and dynamical network biomarkers in respiratory diseases.Clin Transl Med. 2014 Jun 24;3:16. doi: 10.1186/2001-1326-3-16. eCollection 2014. Clin Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 24995123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamical network biomarkers: Theory and applications.Gene. 2022 Jan 15;808:145997. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2021.145997. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Gene. 2022. PMID: 34626720 Review.
Cited by
-
MAPKAPK2, a potential dynamic network biomarker of α-synuclein prior to its aggregation in PD patients.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Mar 16;9(1):41. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00479-z. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 36927756 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the potential miRNA biomarkers based on multi-view networks and reinforcement learning for diseases.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad427. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad427. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 38018913 Free PMC article.
-
Low expression of the dynamic network markers FOS/JUN in pre-deteriorated epithelial cells is associated with the progression of colorectal adenoma to carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 25;21(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03890-5. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36698183 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Cellular Tipping Point in the Inflammation Model of LPS-Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages Through Raman Spectroscopy and the Dynamical Network Biomarker Theory.Molecules. 2025 Feb 17;30(4):920. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040920. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005229 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Dynamical Systems Modeling with Spatiotemporal scRNA-Seq Data Analysis.Entropy (Basel). 2025 Apr 22;27(5):453. doi: 10.3390/e27050453. Entropy (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
