Screening dementia and predicting high dementia risk groups using machine learning
- PMID: 35317343
- PMCID: PMC8900592
- DOI: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.204
Screening dementia and predicting high dementia risk groups using machine learning
Abstract
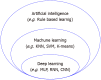
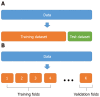
New technologies such as artificial intelligence, the internet of things, big data, and cloud computing have changed the overall society and economy, and the medical field particularly has tried to combine traditional examination methods and new technologies. The most remarkable field in medical research is the technology of predicting high dementia risk group using big data and artificial intelligence. This review introduces: (1) the definition, main concepts, and classification of machine learning and overall distinction of it from traditional statistical analysis models; and (2) the latest studies in mental science to detect dementia and predict high-risk groups in order to help competent researchers who are challenging medical artificial intelligence in the field of psychiatry. As a result of reviewing 4 studies that used machine learning to discriminate high-risk groups of dementia, various machine learning algorithms such as boosting model, artificial neural network, and random forest were used for predicting dementia. The development of machine learning algorithms will change primary care by applying advanced machine learning algorithms to detect high dementia risk groups in the future.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Clinical decision support system; Dementia; Machine learning; Mild cognitive impairment.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Bansal D, Chhikara R, Khanna K, Gupta P. Comparative analysis of various machine learning algorithms for detecting dementia. Procedia Comput Sci . 2018;132:1497–1502.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

