Clinical Effect of Revascularization Strategies and Pharmacologic Treatment on Long-Term Results in Patients with Advanced Peripheral Artery Disease with TASC C and D Femoropopliteal Lesions
- PMID: 35317345
- PMCID: PMC8916894
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3741967
Clinical Effect of Revascularization Strategies and Pharmacologic Treatment on Long-Term Results in Patients with Advanced Peripheral Artery Disease with TASC C and D Femoropopliteal Lesions
Abstract
Background: This study was to assess the clinical outcome and associated parameters of endovascular therapy (EVT group) and bypass surgery (bypass group) in patients with long femoropopliteal TransAtlantic Inter-Society Consensus II (TASC II) C and D peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Methods: 187 patients who underwent successful EVT or bypass surgery were assessed. The endpoints included the events of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and lower-extremity amputation (LEA), 3-year primary patency, and 3-year amputation-free survival (AFS).
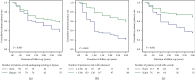
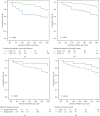
Results: The 3-year primary and secondary patency rates were better in the bypass group (P=0.007 and P=0.039, respectively), while the incidences of LEA, new CVD events, and mortality were comparable between groups. Weighted multivariate Cox analyses showed that cilostazol treatment (hazard ratio (HR): 0.46, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.3-0.72, P=0.001), statin treatment (HR: 0.54, 95% CI: 0.33-0.9, P=0.014), and direct revascularization (DR) (HR: 0.47, 95% CI: 0.29-0.74, P=0.001) were predictive factors of 3-year primary patency. Kaplan-Meier curve analyses of time-to-primary cumulative AFS showed that nondiabetes mellitus, mild PAD, and cilostazol and statin treatment were correlated with a superior 3-year AFS (log rank test, P=0.001, P < 0.001, P=0.009, and P=0.044, respectively).
Conclusions: Endovascular stenting based on the angiosome concept and bypass surgery provide comparable benefits for the treatment of long, advanced femoropopliteal lesions after a short follow-up period, whereas cilostazol therapy for more than 3 months, aggressive treatment of dyslipidemia, and surgical revascularization were associated with higher primary patency.
Copyright © 2022 Chiu-Yang Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Endovascular Therapy with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent and Femoral-Popliteal Bypass for Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus II C and D Femoropopliteal Lesions.Ann Vasc Surg. 2019 May;57:137-143. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2018.09.024. Epub 2018 Nov 27. Ann Vasc Surg. 2019. PMID: 30500627
-
Comparison of surgical bypass with angioplasty and stenting of superficial femoral artery disease.J Vasc Surg. 2014 Jan;59(1):129-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2013.05.100. Epub 2013 Jul 24. J Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 23891488
-
Comparison of long-term outcome after endovascular therapy versus bypass surgery in claudication patients with Trans-Atlantic Inter-Society Consensus-II C and D femoropopliteal disease.Circ J. 2014;78(2):457-64. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-13-1147. Epub 2013 Nov 29. Circ J. 2014. PMID: 24292129 Clinical Trial.
-
A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Efficacy and Safety of Cilostazol Prescription in Patients With Femoropopliteal Peripheral Artery Disease After Endovascular Therapy.J Endovasc Ther. 2024 Apr 9:15266028241241248. doi: 10.1177/15266028241241248. Online ahead of print. J Endovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 38590247 Review.
-
A meta-analysis to compare Dacron versus polytetrafluroethylene grafts for above-knee femoropopliteal artery bypass.J Vasc Surg. 2014 Aug;60(2):506-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.05.049. Epub 2014 Jun 25. J Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24973288 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between statin intensity and femoropopliteal stent primary patency in peripheral arterial disease.CVIR Endovasc. 2024 Aug 3;7(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s42155-024-00472-4. CVIR Endovasc. 2024. PMID: 39096322 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
