The Duties of Dermatologists During COVID-19 Pandemic in Turkey: Results of a Nationwide Survey
- PMID: 35317369
- PMCID: PMC8907688
- DOI: 10.14744/SEMB.2021.67750
The Duties of Dermatologists During COVID-19 Pandemic in Turkey: Results of a Nationwide Survey
Abstract
Objectives: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has led to a reorganization of health services throughout many countries. In this study, we aimed to get an overview of the duties of the dermatologists during COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey. In light of the results, we aimed to determine the aspects of Turkish dermatology practice which might require innovation.
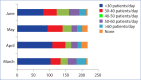
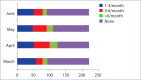
Methods: Dermatologists across Turkey were asked to fill in an online 11-item questionnaire survey, investigating their duty/duties (dermatology outpatient and inpatient clinics, pandemic outpatient and inpatient clinics, emergency, etc.) month by month during March-June 2020.
Results: A total of 217 dermatologists participated in the survey. Vast majority (91-98%) of the participants reported that they performed dermatology outpatient visits. While 41.5-56.2% of participants were redeployed to pandemic inpatient clinics, 12.9-29% were mobilized to pandemic outpatient clinics. Each month, at least 90% of the residents that participated in the questionnaire reported that they were recruited to pandemic inpatient clinics.
Conclusion: As the impact of COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing in Turkey, these data should be taken into consideration to rapidly implement new measures in Turkish dermatology practices such as a referral system for dermatology outpatient visits to equitably distribute dermatology services, widespread use of telemedicine, and virtual educations of residents.
Keywords: Coronavirus; dermatology; pandemic.
Copyright © by The Medical Bulletin of Sisli Etfal Hospital.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic in dermatology outpatient clinics in Turkey: A survey study.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021 Aug;20(8):2382-2386. doi: 10.1111/jocd.14297. Epub 2021 Jun 25. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34133815 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of COVID-19 on Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation in Turkey in the first month of pandemic.Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020 Jul 7;66(3):244-251. doi: 10.5606/tftrd.2020.6800. eCollection 2020 Sep. Turk J Phys Med Rehabil. 2020. PMID: 33089080 Free PMC article.
-
Views and experiences of dermatologists in Turkey about teledermatology during the COVID-19 pandemic.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Oct;19(10):2460-2463. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13677. Epub 2020 Sep 4. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32881217 Free PMC article.
-
Changing paradigms of dermatology practice in developing nations in the shadow of COVID-19: Lessons learnt from the pandemic.Dermatol Ther. 2020 Jul;33(4):e13472. doi: 10.1111/dth.13472. Epub 2020 May 28. Dermatol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32347612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of physician assistants in the delivery of dermatologic health care.Dermatol Clin. 2000 Apr;18(2):297-302. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8635(05)70175-3. Dermatol Clin. 2000. PMID: 10791156 Review.
References
-
- Shipchandler TZ, Nesemeier BR, Schmalbach CE, Ting JY. Otolaryngologists' role in redeployment during the COVID-19 pandemic: a commentary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;163:94–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials