A Novel Tissue Atlas and Online Tool for the Interrogation of Small RNA Expression in Human Tissues and Biofluids
- PMID: 35317387
- PMCID: PMC8934391
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.804164
A Novel Tissue Atlas and Online Tool for the Interrogation of Small RNA Expression in Human Tissues and Biofluids
Abstract
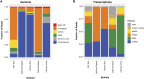
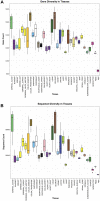
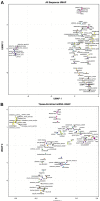
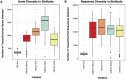
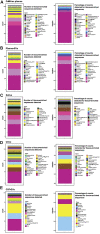
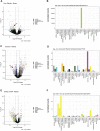
One promising goal for utilizing the molecular information circulating in biofluids is the discovery of clinically useful biomarkers. Extracellular RNAs (exRNAs) are one of the most diverse classes of molecular cargo, easily assayed by sequencing and with expressions that rapidly change in response to subject status. Despite diverse exRNA cargo, most evaluations from biofluids have focused on small RNA sequencing and analysis, specifically on microRNAs (miRNAs). Another goal of characterizing circulating molecular information, is to correlate expression to injuries associated with specific tissues of origin. Biomarker candidates are often described as being specific, enriched in a particular tissue or associated with a disease process. Likewise, miRNA data is often reported to be specific, enriched for a tissue, without rigorous testing to support the claim. Here we provide a tissue atlas of small RNAs from 30 different tissues and three different blood cell types. We analyzed the tissues for enrichment of small RNA sequences and assessed their expression in biofluids: plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and saliva. We employed published data sets representing physiological (resting vs. acute exercise) and pathologic states (early- vs. late-stage liver fibrosis, and differential subtypes of stroke) to determine differential tissue-enriched small RNAs. We also developed an online tool that provides information about exRNA sequences found in different biofluids and tissues. The data can be used to better understand the various types of small RNA sequences in different tissues as well as their potential release into biofluids, which should help in the validation or design of biomarker studies.
Keywords: cerebrospinal fluid; extracellular RNA; extracellular vesicle; plasma; saliva; small RNA; tissue atlas; urine.
Copyright © 2022 Alsop, Meechoovet, Kitchen, Sweeney, Beach, Serrano, Hutchins, Ghiran, Reiman, Syring, Hsieh, Courtright-Lim, Valkov, Whitsett, Rakela, Pockros, Rozowsky, Gallego, Huentelman, Shah, Nakaji, Kalani, Laurent, Das and Van Keuren-Jensen.
Conflict of interest statement
KV and SD are members of the scientific advisory board at Dyrnamix. Their involvement in this company had no bearing on the work performed in this manuscript. KV is on the scientific advisory board of HTG. Her involvement has no bearing on this work. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures