Validation of the PAGE-B score to predict hepatocellular carcinoma risk in caucasian chronic hepatitis B patients on treatment
- PMID: 35317422
- PMCID: PMC8900546
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i6.665
Validation of the PAGE-B score to predict hepatocellular carcinoma risk in caucasian chronic hepatitis B patients on treatment
Abstract
Background: Several risk scores have been developed to predict hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) risk in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients. The majority of risk scores are based on pretreatment variables that are no longer considered risk factors for HCC development due to the suppression of hepatitis B virus replication early in the course of potent antiviral treatment in most patients. The PAGE-B score, which is based on platelet levels, age and sex, has been shown to accurately predict HCC risk in CHB patients on antiviral treatment in various populations.
Aim: We aimed to evaluate the PAGE-B score in predicting HCC risk in Turkish CHB patients on antiviral treatment.
Methods: In this study, we recruited 742 CHB patients who had been treated with tenofovir disoproxil fumarate or entecavir for ≥ 1 year. Risk groups were determined according to the PAGE-B scores as follows: ≤ 9, low; 10-17, moderate and ≥ 18, high. The cumulative HCC incidences in each risk group were computed using Kaplan-Meier analysis and were compared using the log-rank test. The accuracy of the PAGE-B score in predicting HCC risk was evaluated using a time-dependent area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve at all study time points. Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to assess the risk factors for HCC development.
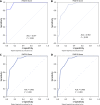
Results: The mean follow-up time was 54.7 ± 1.2 mo. HCC was diagnosed in 26 patients (3.5%). The cumulative HCC incidences at 1, 3, 5 and 10 years were 0%, 0%, 0% and 0.4% in the PAGE-B low-risk group; 0%, 1.2%, 1.5% and 2.1% in the PAGE-B moderate-risk group; and 5%, 11.7%, 12.5%, and 15% in the PAGE-B high-risk group, respectively (log-rank P < 0.001). The AUROCs of the PAGE-B score in the prediction of HCC development at 1, 3, 5 and 10 years were 0.977, 0.903, 0.903 and 0.865, respectively. In the multivariable analysis, older age, male sex, lower platelet levels, presence of cirrhosis, and absence of alanine aminotransferase normalization at month 6 were associated with HCC development (all P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The PAGE-B score is a practical tool to predict HCC risk in Turkish patients with CHB and may be helpful to improve surveillance strategies.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis B; Hepatocellular carcinoma; PAGE-B score; Surveillance.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modified PAGE-B score predicts the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asians with chronic hepatitis B on antiviral therapy.J Hepatol. 2018 Nov;69(5):1066-1073. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.07.018. Epub 2018 Aug 1. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30075230
-
Reassessing the accuracy of PAGE-B-related scores to predict hepatocellular carcinoma development in patients with chronic hepatitis B.J Hepatol. 2020 May;72(5):847-854. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.005. Epub 2019 Dec 16. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31857194
-
Validation of the HCC-RESCUE score to predict hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Caucasian chronic hepatitis B patients under entecavir or tenofovir therapy.J Viral Hepat. 2021 May;28(5):826-836. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13485. Epub 2021 Feb 24. J Viral Hepat. 2021. PMID: 33586270
-
Magnitude of and prediction for risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B taking entecavir or tenofovir therapy: A systematic review.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;35(10):1684-1693. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15078. Epub 2020 May 17. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32343431
-
Clinical utility of hepatocellular carcinoma risk scores in chronic hepatitis B.Liver Int. 2020 Mar;40(3):484-495. doi: 10.1111/liv.14334. Epub 2020 Jan 7. Liver Int. 2020. PMID: 31884726 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Term Survival and Curative-Intent Treatment in Hepatitis B or C Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Diagnosed during Screening.Biology (Basel). 2022 Nov 1;11(11):1597. doi: 10.3390/biology11111597. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358298 Free PMC article.
-
HBX Multi-Mutations Combined With Traditional Screening Indicators to Establish a Nomogram Contributes to Precisely Stratify the High-Risk Population of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(5):e70748. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70748. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40042093 Free PMC article.
-
Results in chronic hepatitis B patients using tenofovir and entecavir for at least 10 years; HBV clearance rare, disease outcomes good: An observational cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jun 6;104(23):e42766. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042766. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 40489803 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of PAGE-B Score for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients: Reliability, Validity, and Responsiveness.Biomedicines. 2024 Jun 5;12(6):1260. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061260. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization and Detection Strategy Exploration in Cryptogenic Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Insights From a Super-Aged Region in Japan.Cancer Med. 2025 Jan;14(2):e70490. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70490. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 39846235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years for 29 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4:1553–1568. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, Heimbach JK. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68:723–750. - PubMed
-
- Yang HI, Yuen MF, Chan HL, Han KH, Chen PJ, Kim DY, Ahn SH, Chen CJ, Wong VW, Seto WK REACH-B Working Group. Risk estimation for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B (REACH-B): development and validation of a predictive score. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:568–574. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

