Effects and early diagnostic value of lncRNA H19 on sepsis-induced acute lung injury
- PMID: 35317444
- PMCID: PMC8908336
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11208
Effects and early diagnostic value of lncRNA H19 on sepsis-induced acute lung injury
Abstract
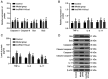
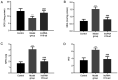
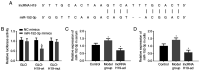
Sepsis is an immune disease induced by microbial invasion. The molecular mechanism and value of long non-coding H19 (lncRNA H19) in sepsis remain largely unknown. The present study aimed to investigate the effects and early diagnostic value of lncRNA H19 on sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI). Serum samples from 85 septic patients and 76 healthy individuals were collected, and the expression of lncRNA H19 was assessed by the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were subjected to cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) in order to construct models of sepsis-induced ALI. A total of 18 successfully modeled rats were randomly allocated into an lncRNA H19-ad group and a model group, and another 9 healthy SD rats from the same batch were selected as a control group. The samples of serum and lung tissue were collected. lncRNA H19 expression was quantified by qPCR, and levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-17, caspase-3, caspase-9, B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), and BCL2-associated X (Bax) were measured by western blotting. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was employed to assess the diagnostic value of lncRNA H19 for septic patients. lncRNA H19 was downregulated in sepsis. Upregulation of lncRNA H19 inhibited TNF-α, IL-6, IL-17, caspase-3, caspase-9 and Bax and increased Bcl-2. The AUC of lncRNA H19 for early diagnosis of sepsis was 0.8197 (95% CI, 0.77 to 0.91). lncRNA H19 alleviated sepsis-induced ALI by inhibiting pulmonary apoptosis and inflammation, serving as a biochemical marker and therapeutic target for sepsis.
Keywords: acute lung injury; early diagnosis; long non-coding RNA H19; sepsis.
Copyright: © Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
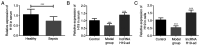

Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA H19 as a diagnostic marker in peripheral blood of patients with sepsis.Am J Transl Res. 2021 Apr 15;13(4):2923-2930. eCollection 2021. Am J Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34017457 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of lncRNA HOTAIR on acute kidney injury in sepsis rats through regulating miR-34a/Bcl-2 pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Apr;23(8):3512-3519. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201904_17717. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31081107
-
[Electroacupuncture protects septic rats from acute lung injury through the JAK1/STAT3 pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Nov 30;40(11):1662-1667. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.11.20. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33243749 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Heat Shock Protein A12B Protects Vascular Endothelial Cells Against Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(1):156-168. doi: 10.1159/000477308. Epub 2017 May 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28535510
-
Targeting non-coding RNA H19: A potential therapeutic approach in pulmonary diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 16;13:978151. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.978151. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Diagnostic Utility of Host RNA Biosignatures in Adult Patients With Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Crit Care Explor. 2025 Jan 31;7(2):e1212. doi: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000001212. eCollection 2025 Feb 1. Crit Care Explor. 2025. PMID: 39888601 Free PMC article.
-
The Renshen Chishao Decoction Could Ameliorate the Acute Lung Injury but Could Not Reduce the Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Formation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Aug 29;2022:7784148. doi: 10.1155/2022/7784148. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36072401 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Predictive Value of LncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 in Sepsis and Its Regulatory Role in Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Oct;24(10):1125-1138. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09903-z. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39085530
-
Identification and Evaluation of Hub Long Non-Coding RNAs and mRNAs in PM2.5-Induced Lung Cell Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 22;26(3):911. doi: 10.3390/ijms26030911. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940682 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1688. doi: 10.3390/life14121688. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768394 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lever A, Mackenzie I. Sepsis: Definition, epidemiology, and diagnosis. BMJ. 2007;335:879–883. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39346.495880.AE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Martin-Loeches I, Guia MC, Vallecoccia MS, Suarez D, Ibarz M, Irazabal M, Ferrer R, Artigas A. Risk factors for mortality in elderly and very elderly critically ill patients with sepsis: A prospective, observational, multicenter cohort study. Ann Intensive Care. 2019;9(26) doi: 10.1186/s13613-019-0495-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
