CircRHBDD1 augments metabolic rewiring and restricts immunotherapy efficacy via m6A modification in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35317519
- PMCID: PMC8908059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.02.021
CircRHBDD1 augments metabolic rewiring and restricts immunotherapy efficacy via m6A modification in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
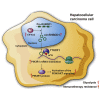
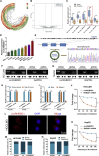
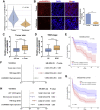
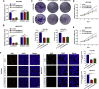
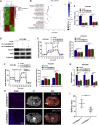
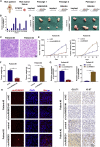
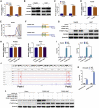
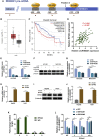
Circular RNAs are a class of highly conserved RNAs with stable covalently closed circular structures. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer cells reshapes the tumor microenvironment and can suppress antitumor immunity. Here, we discovered a novel circular RNA, termed circRHBDD1, which augments aerobic glycolysis and restricts anti-PD-1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Mechanistic studies revealed that circRHBDD1 recruits the m6A reader YTHDF1 to PIK3R1 mRNA and accelerates the translation of PIK3R1 in an m6A-dependent manner. EIF4A3-mediated exon back-splicing contributes to the upregulation of circRHBDD1. Moreover, circRHBDD1 is highly expressed in anti-PD-1 responder HCC patients, and targeting circRHBDD1 improves anti-PD-1 therapy in an immune-competent mouse model. Overall, these findings illustrate the metabolic importance of the circRHBDD1/YTHDF1/PIK3R1 axis in HCC and show that suppression of circRHBDD1 may bolster the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy for HCC treatment.
Keywords: PIK3R1; YTHDF1; circular RNA; glycolysis; hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Llovet J.M., Kelley R.K., Villanueva A., Singal A.G., Pikarsky E., Roayaie S., Lencioni R., Koike K., Zucman-Rossi J., Finn R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2021;7:6. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

