MiR-106b-5p regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by binding to HPGD
- PMID: 35317779
- PMCID: PMC8941792
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09404-8
MiR-106b-5p regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by binding to HPGD
Abstract
Background: Several studies have documented the key role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Although the expression of the 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (HPGD) gene and miR-106b-5p are reportedly linked to cancer progression, their underlying mechanisms in ESCC remain unclear.
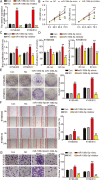
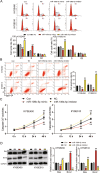
Methods: mRNA and miRNA expression in ESCC tissues and cells were analyzed using RT-qPCR. Luciferase and RNA pull-down assays were used to identify the interaction between miR-106b-5p and HPGD. Xenograft and pulmonary metastasis models were used to assess tumor growth and metastasis. CCK-8, BrdU, colony formation, adhesion, cell wound healing, Transwell, and caspase-3/7 activity assays, and flow cytometry and western blot analyses were used to examine the function of miR-106-5p and HPGD in ESCC cell lines.
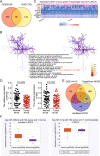
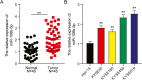
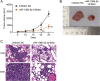
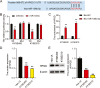
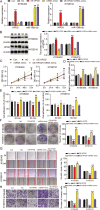
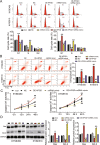
Results: The findings revealed that miR-106b-5p expression was upregulated in ESCC tissues and cell lines. miR-106b-5p augmented cellular proliferation, colony formation, adhesion, migration, invasion, and proportion of cells in the S-phase, but reduced apoptosis and the proportion of cells in G1-phase. Silencing of miR-106-5p inhibited tumor growth in vivo and pulmonary metastasis. Although HPGD overexpression suppressed proliferation, colony formation, adhesion, migration, and invasion of ESCC cells, it promoted apoptosis and caused cell cycle arrest of the ESCC cells. The results also indicated a direct interaction of HPGD with miR-106b-5p in ESCC cells. Furthermore, miR-106b-5p inhibited HPGD expression, thereby suppressing ESCC tumorigenesis.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that miR-106b-5p enhances proliferation, colony formation, adhesion, migration, and invasion, and induces the cycle progression, but represses apoptosis of ESCC cells by targeting HPGD. This suggests that the miR-106b-5p/HPGD axis may serve as a promising target for the diagnosis and treatment of ESCC.
Keywords: 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase; Adhesion; Apoptosis; Cell cycle; Colony formation; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; Invasion; MiR-106b-5p; Migration; Proliferation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs: A novel signature in the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1497-1523. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1497. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of Long Noncoding RNA SNHG6 Inhibits Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression via miR-186-5p/HIF1α Axis.Dig Dis Sci. 2020 Oct;65(10):2844-2852. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-06012-8. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2020. Retraction in: Dig Dis Sci. 2025 Jan;70(1):429. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08807-w. PMID: 31853782 Retracted.
-
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000654 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating the miR-149-5p/IL-6/STAT3 pathway.IUBMB Life. 2020 Mar;72(3):426-439. doi: 10.1002/iub.2202. Epub 2019 Nov 28. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 31778020
-
CircDUSP16 Contributes to Cell Development in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Regulating miR-497-5p/TKTL1 Axis.J Surg Res. 2021 Apr;260:64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.11.052. Epub 2020 Dec 14. J Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 33326930
-
The tumor suppressor role and epigenetic regulation of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) in cancer and tumor microenvironment (TME).Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Apr;268:108826. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108826. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39971253 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-210 Mediated Hypoxic Responses in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.ACS Omega. 2024 Nov 20;9(48):47872-47883. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08947. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39651070 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variants in oncogenic miRNA and 3' untranslated region of tumor suppressor genes: emerging insight into cancer genetics.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 30;42(8):303. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02873-4. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40587016 Review.
-
Bioinformatics and systems biology to identify underlying common pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease and stenosis of arteriovenous fistula.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 1;26(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04239-4. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40597829 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs: A novel signature in the metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 21;30(11):1497-1523. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i11.1497. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38617454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hpgd affects the progression of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by regulating vascular remodeling.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Apr 13;23(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02401-y. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37055764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsushima K, Isomoto H, Yamaguchi N, Inoue N, Machida H, Nakayama T, Hayashi T, Kunizaki M, Hidaka S, Nagayasu T, et al. MiRNA-205 modulates cellular invasion and migration via regulating zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2 expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Transl Med. 2011;9:30. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-30. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

