Treatment strategies for postviral olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review
- PMID: 35317886
- PMCID: PMC8984764
- DOI: 10.2500/aap.2022.43.210107
Treatment strategies for postviral olfactory dysfunction: A systematic review
Abstract
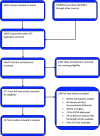
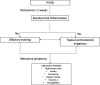
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been associated with a dramatic increase in postviral olfactory dysfunction (PVOD) among patients who are infected. A contemporary evidence-based review of current treatment options for PVOD is both timely and relevant to improve patient care. Objective: This review seeks to impact patient care by qualitatively reviewing available evidence in support of medical and procedural treatment options for PVOD. Systematic evaluation of data quality and of the level of evidence was completed to generate current treatment recommendations. Methods: A systematic review was conducted to identify primary studies that evaluated treatment outcomes for PVOD. A number of medical literature data bases were queried from January 1998 to May 2020, with completion of subsequent reference searches of retrieved articles to identify all relevant studies. Validated tools for the assessment of bias among both interventional and observational studies were used to complete quality assessment. The summary level of evidence and associated outcomes were used to generate treatment recommendations. Results: Twenty-two publications were identified for qualitative review. Outcomes of alpha-lipoic acid, intranasal and systemic corticosteroids, minocycline, zinc sulfate, vitamin A, sodium citrate, caroverine, intranasal insulin, theophylline, and Gingko biloba are reported. In addition, outcomes of traditional Chinese acupuncture and olfactory training are reviewed. Conclusion: Several medical and procedural treatments may expedite the return of olfactory function after PVOD. Current evidence supports olfactory training as a first-line intervention. Additional study is required to define specific treatment recommendations and expected outcomes for PVOD in the setting of COVID-19.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical