Translating recent advances in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia to the clinic
- PMID: 35318270
- PMCID: PMC8973851
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.349368.122
Translating recent advances in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia to the clinic
Abstract
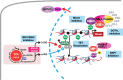
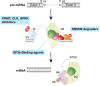
Despite FDA approval of nine new drugs for patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in the United States over the last 4 years, AML remains a major area of unmet medical need among hematologic malignancies. In this review, we discuss the development of promising new molecular targeted approaches for AML, including menin inhibition, novel IDH1/2 inhibitors, and preclinical means to target TET2, ASXL1, and RNA splicing factor mutations. In addition, we review progress in immune targeting of AML through anti-CD47, anti-SIRPα, and anti-TIM-3 antibodies; bispecific and trispecific antibodies; and new cellular therapies in development for AML.
Keywords: ASXL1; IDH1; IDH2; RNA splicing; TET2; acute myeloid leukemia; menin; myelodysplastic syndromes.
© 2022 Bewersdorf and Abdel-Wahab; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


References
-
- Armand P, Zinzani PLL, Palcza J, Healy JA, Nahar A, Marinello P, Gregory GP. 2019. Phase 1–2 study of pembrolizumab combined with the anti-LAG-3 antibody MK-4280 for the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Blood 134: 1548. 10.1182/blood-2019-127474 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
