Effects of depression on employment and social outcomes: a Mendelian randomisation study
- PMID: 35318279
- PMCID: PMC9118074
- DOI: 10.1136/jech-2021-218074
Effects of depression on employment and social outcomes: a Mendelian randomisation study
Abstract
Background: Depression is associated with socioeconomic disadvantage. However, whether and how depression exerts a causal effect on employment remains unclear. We used Mendelian randomisation (MR) to investigate whether depression affects employment and related outcomes in the UK Biobank dataset.
Methods: We selected 227 242 working-age participants (40-64 in men, 40-59 years for women) of white British ethnicity/ancestry with suitable genetic data in the UK Biobank study. We used 30 independent genetic variants associated with depression as instruments. We conducted observational and two-sample MR analyses. Outcomes were employment status (employed vs not, and employed vs sickness/disability, unemployment, retirement or caring for home/family); weekly hours worked (among employed); Townsend Deprivation Index; highest educational attainment; and household income.
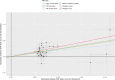
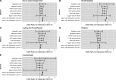
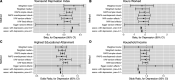
Results: People who had experienced depression had higher odds of non-employment, sickness/disability, unemployment, caring for home/family and early retirement. Depression was associated with reduced weekly hours worked, lower household income and lower educational attainment, and increased deprivation. MR analyses suggested depression liability caused increased non-employment (OR 1.16, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.26) and sickness/disability (OR 1.56, 95% CI 1.34 to 1.82), but was not causal for caring for home/family, early retirement or unemployment. There was little evidence from MR that depression affected weekly hours worked, educational attainment, household income or deprivation.
Conclusions: Depression liability appears to cause increased non-employment, particularly by increasing disability. There was little evidence of depression affecting early retirement, hours worked or household income, but power was low. Effective treatment of depression might have important economic benefits to individuals and society.
Keywords: Keywords.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: SVK reports grants from the Medical Research Council, the Health Foundation and the Scottish Government Chief Scientist Office during the conduct of this study.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators . Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2018;392:1789–858. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32279-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- England NHS. The five year forward view for mental health. A report from the independent mental health Taskforce to the NHS in England. London: NHS England, 2016.
-
- Paul KI, Moser K. Unemployment impairs mental health: meta-analyses. J Vocat Behav 2009;74:264–82. 10.1016/j.jvb.2009.01.001 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 220857/Z/20/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 104036/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00011/7/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SPHSU13/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MRC_PC_13027/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SCAF/15/02/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17209/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_13027/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12017/13/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- SPHSU17/CSO_/Chief Scientist Office/United Kingdom
- MR/M020894/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00022/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
