Gut Microbiota Alteration Influences Colorectal Cancer Metastasis to the Liver by Remodeling the Liver Immune Microenvironment
- PMID: 35318288
- PMCID: PMC9289841
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl210177
Gut Microbiota Alteration Influences Colorectal Cancer Metastasis to the Liver by Remodeling the Liver Immune Microenvironment
Abstract
Background/aims: This study aimed to explore the effect of gut microbiota-regulated Kupffer cells (KCs) on colorectal cancer (CRC) liver metastasis.
Methods: A series of in vivo and in vitro researches were showed to demonstrate the gut microbiota and its possible mechanism in CRC liver metastasis.
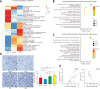
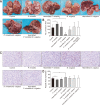
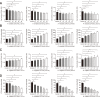
Results: Fewer liver metastases were identified in the ampicillin-streptomycin-colistin and colistin groups. Increased proportions of Parabacteroides goldsteinii, Bacteroides vulgatus, Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron, and Bacteroides uniformis were observed in the colistin group. The significant expansion of KCs was identified in the ampicillin-streptomycin-colistin and colistin groups. B. vulgatus levels were positively correlated with KC levels. More liver metastases were observed in the vancomycin group. An increased abundance of Parabacteroides distasonis and Proteus mirabilis and an obvious reduction of KCs were noted in the vancomycin group. P. mirabilis levels were negatively related to KC levels. The number of liver metastatic nodules was increased in the P. mirabilis group and decreased in the B. vulgatus group. The number of KCs decreased in the P. mirabilis group and increased in the B. vulgatus group. In vitro, as P. mirabilis or B. vulgatus doses increased, there was an opposite effect on KC proliferation in dose- and time-dependent manners. P. mirabilis induced CT26 cell migration by controlling KC proliferation, whereas B. vulgatus prevented this migration.
Conclusions: An increased abundance of P. mirabilis and decreased amount of B. vulgatus play key roles in CRC liver metastasis, which might be related to KC reductions in the liver.
Keywords: Colorectal neoplasms; Gastrointestinal microbiome; Kupffer cells; Liver metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The renin angiotensin system regulates Kupffer cells in colorectal liver metastases.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Aug;14(8):720-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.25092. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23792575 Free PMC article.
-
Bimodal role of Kupffer cells during colorectal cancer liver metastasis.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Jul;14(7):606-13. doi: 10.4161/cbt.24593. Epub 2013 May 10. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23792646 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between gut microbiota and metastasis in colorectal cancer: implication of neutrophil extracellular traps.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 23;14:1296783. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1296783. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37936694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacteroides vulgatus and Bacteroides dorei Reduce Gut Microbial Lipopolysaccharide Production and Inhibit Atherosclerosis.Circulation. 2018 Nov 27;138(22):2486-2498. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.033714. Circulation. 2018. PMID: 30571343
-
Gut microbiota and colorectal cancer metastasis.Cancer Lett. 2023 Feb 28;555:216039. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.216039. Epub 2022 Dec 15. Cancer Lett. 2023. PMID: 36528182 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of gut microbiota in colorectal liver metastasis through the gut-liver axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 13;13:1563184. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1563184. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40181829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic use during radical surgery in stage I-III colorectal cancer: correlation with outcomes?BMC Cancer. 2024 Jun 26;24(1):769. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12550-w. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38926655 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of colorectal cancer progression-associated intestinal microbiome and predictive signature construction.J Transl Med. 2023 Jun 8;21(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04119-1. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37291572 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mechanisms progress of colorectal cancer liver metastasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 8;13:1081585. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1081585. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36568117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preoperative albumin-bilirubin score as a prognostic indicator in patients with stage III colon cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 1;12(1):14910. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19329-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36050367 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

