Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Conditioned Medium of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ATMSC)-Treated Fresh Frozen Plasma
- PMID: 35318298
- PMCID: PMC8958862
- DOI: 10.12659/MSMBR.933726
Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Conditioned Medium of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ATMSC)-Treated Fresh Frozen Plasma
Abstract
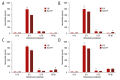
BACKGROUND Inflammation is the body's first response to an illness that causes irritation or infection. Inflammation is tightly correlated with aging, which is a progressive degenerative process. Conditioned medium (CM) from adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (CM-ATMSCs) has been shown to stimulate collagen synthesis and dermal fibroblast migration, as well as reduce wrinkles and improve wound healing. This study aimed to observe the production of inflammatory modulators - interleukin (IL)-1alpha, IL-6, IL-10, and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kappaB) - in CM-ATMSCs treated with fresh frozen plasma (FFP) at passages 3 (P3), 7, 11, and 15. MATERIAL AND METHODS ATMSCs P3 were obtained from liposuction of female donors, and the CM from ATMSCs was collected. Measurement of these cytokines was performed with ELISA. RESULTS At many passages, IL-6, a proinflammatory modulator, was discovered to be the most powerful modulator among FFP- and non-FFP-treated cells. However, CM-ATMSCs treated with FFP and in the late passage have significant differences (P<0.05) compared to non-FFP treatments and in other passages in their effects on secretion of inflammatory modulators. CONCLUSIONS In conclusion, CM-ATMSC has the potential to secrete proinflammatory modulators.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
The neuroprotective effect of rat adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium on cortical neurons using an in vitro model of SCI inflammation.Neurol Res. 2018 Apr;40(4):258-267. doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1432266. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Neurol Res. 2018. PMID: 29384015
-
[Effects of hypoxia-pretreated rat adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium on wound healing of rats with full-thickness defects].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Sep 20;36(9):803-812. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20200508-00258. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32972065 Chinese.
-
Regeneration of full-thickness skin defects by differentiated adipose-derived stem cells into fibroblast-like cells by fibroblast-conditioned medium.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017 Apr 20;8(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0520-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28427476 Free PMC article.
-
Transplantation of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell (ATMSC) Expressing Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Reduces Bone Loss in Ovariectomized Osteoporosis Mice.Hum Gene Ther. 2017 Feb;28(2):179-189. doi: 10.1089/hum.2016.069. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Hum Gene Ther. 2017. PMID: 27802778 Review.
-
Hair Regeneration Therapy: Application of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(7):531-534. doi: 10.2174/1574888X12666170522114307. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28530535 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Response to Article "Hypoxia Effects in Intervertebral Disc-Derived Stem Cells and Discus Secretomes: An in vitro Study" [Letter].Stem Cells Cloning. 2022 Oct 20;15:63-64. doi: 10.2147/SCCAA.S391016. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Cloning. 2022. PMID: 36300159 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potential antiaging activity of secretome gel of human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells (hWJ-MSCs) in UV-induced mice models.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(7):868-878. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2024.70825.15385. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38800010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amani H, Shahbazi MA, D’Amico C, et al. Microneedles for painless transdermal immunotherapeutic applications. J Control Release. 2021;330:185–217. - PubMed
-
- Choi SA, Lee JY, Wang KC, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: characteristics and therapeutic potential as cellular vehicles for prodrug gene therapy against brainstem gliomas. Eur J Cancer. 2011;48:129–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

