Antibody drug conjugate: the "biological missile" for targeted cancer therapy
- PMID: 35318309
- PMCID: PMC8941077
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-00947-7
Antibody drug conjugate: the "biological missile" for targeted cancer therapy
Abstract
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is typically composed of a monoclonal antibody (mAbs) covalently attached to a cytotoxic drug via a chemical linker. It combines both the advantages of highly specific targeting ability and highly potent killing effect to achieve accurate and efficient elimination of cancer cells, which has become one of the hotspots for the research and development of anticancer drugs. Since the first ADC, Mylotarg® (gemtuzumab ozogamicin), was approved in 2000 by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), there have been 14 ADCs received market approval so far worldwide. Moreover, over 100 ADC candidates have been investigated in clinical stages at present. This kind of new anti-cancer drugs, known as "biological missiles", is leading a new era of targeted cancer therapy. Herein, we conducted a review of the history and general mechanism of action of ADCs, and then briefly discussed the molecular aspects of key components of ADCs and the mechanisms by which these key factors influence the activities of ADCs. Moreover, we also reviewed the approved ADCs and other promising candidates in phase-3 clinical trials and discuss the current challenges and future perspectives for the development of next generations, which provide insights for the research and development of novel cancer therapeutics using ADCs.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
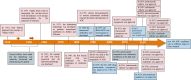

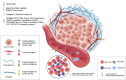

References
-
- Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Loadman P. Anticancer drug development. Br. J. Cancer. 2002;86:1665–1666.
-
- Gilman A, Philips FS. The biological actions and therapeutic applications of the B-chloroethyl amines and sulfides. Science. 1946;103:409–436. - PubMed
-
- Heidelberger C, et al. Fluorinated pyrimidines, a new class of tumour-inhibitory compounds. Nature. 1957;179:663–666. - PubMed
-
- Norris RE, Adamson PC. Clinical potency of methotrexate, aminopterin, talotrexin and pemetrexed in childhood leukemias. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010;65:1125–1130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

