[Eustachian tube dysfunction after cleft palate surgery : Use of the latest diagnostics]
- PMID: 35318498
- PMCID: PMC9242949
- DOI: 10.1007/s00106-022-01147-z
[Eustachian tube dysfunction after cleft palate surgery : Use of the latest diagnostics]
Abstract
Objective: In patients with cleft palate, a high incidence of chronic obstructive Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is assumed after surgery. Consequently, an increased rate of retracted eardrum or cholesteatoma is expected. Even though no common standard for investigating ETD is available, the development of objective tests has increased during the past 10 years. This study aimed to investigate the incidence of persisting chronic obstructive ETD in adult patients with cleft palate surgically treated in early childhood by using a combination of diagnostic tools.
Methods: Adult participants with cleft palate repair in early childhood were invited for a follow-up examination and compared to a control group. Examination included tympanometry, tubomanometry, the Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7), and the Eustachian Tube Score 7 (ETS-7).
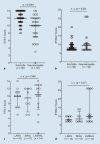
Results: A total of 16 adult patients were re-examined after cleft palate surgery and compared to a control group of 40 healthy individuals. Significant differences were found in the median ETS‑7 (p < 0.0001) score but not in the median ETDQ‑7 (p = 0.09) score. Only 2 of the 32 investigated ears (6%) had pathologic scores in ETS‑7 and ETDQ‑7 (p = 0.09), whereas 5 (31%) cleft palate patients showed symptoms of chronic obstructive ETD according to ETS‑7. No patient had examination findings indicating a requirement for further treatment.
Conclusion: By combining diagnostic tools for ETD, a lower rate of persisting obstructive ETD in adults after cleft palate surgery was found than previously reported. Successful surgical treatment of cleft palate seems to lead to physiological Eustachian tube function in long-term follow up.
Zusammenfassung: FRAGESTELLUNG: Bei Patienten mit einer Lippen-Kiefer-Gaumen-Spalte (LKGS) wird eine hohe Inzidenz von chronisch-obstruktiven Tubenventilationsstörungen auch nach chirurgischem Spaltverschluss angenommen. Folglich ist eine erhöhte Rate von Trommelfellretraktionen oder Cholesteatomen zu erwarten. Ziel dieser Studie war es, mit den aktuellen Methoden die Prävalenz chronisch-obstruktiven Tubenventilationsstörung bei erwachsenen Patienten nach behandelter LKGS zu untersuchen.
Methoden: Es wurden erwachsene Patienten mit LKGS nach chirurgischem Spaltverschluss in der Kindheit eingeschlossen und mit einer Kontrollgruppe verglichen. Eine Nachuntersuchung erfolgte mittels Tympanometrie, Tubenmanometrie, ETDQ‑7 (Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire) und dem Eustachian Tube Score‑7 (ETS-7).
Ergebnisse: Insgesamt 16 Erwachsene nach LKGS-Operation und 40 gesunde Probanden wurden eingeschlossen. Signifikante Unterschiede wurden beim medianen ETS-7-Score (p < 0,0001) gefunden, nicht aber beim medianen ETDQ-7-Score (p = 0,09). Nur 2 der 32 untersuchten Ohren (6 %) wiesen sowohl einen pathologischen ETS‑7 als auch ETDQ‑7 auf. Bei 5 (31 %) LKGS-Patienten ergab sich gemäß ETS‑7 Anhalt für eine Beeinträchtigung der Tubenfunktion. Kein Patient hatte einen Untersuchungsbefund, der eine weitere Behandlung notwendig machte.
Schlussfolgerung: Durch die Kombination von Diagnoseinstrumenten für chronisch-obstruktive Tubenventilationsstörungen wurde eine geringere Rate an persistierenden chronisch-obstruktiven Tubenventilationsstörungen bei Erwachsenen nach LKGS-Operation gefunden als bisher berichtet. Eine erfolgreiche chirurgische Behandlung der LKGS scheint nach langfristiger Nachbeobachtung zu einer physiologischen Funktion der Tuba auditiva zu führen.
Keywords: Chronic obstructive Eustachian tube; Diagnostic tool; ETDQ‑7; ETS‑7.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Similar articles
-
A novel diagnostic tool for chronic obstructive eustachian tube dysfunction—the eustachian tube score.Laryngoscope. 2015 Mar;125(3):703-8. doi: 10.1002/lary.24922. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Laryngoscope. 2015. PMID: 25215457
-
Clinical value of the Eustachian Tube Function Scoring System T-ETDQ: a prospective diagnostic study.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 May;279(5):2223-2230. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07108-6. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34590179 Review.
-
Validating the 7-item Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire in Danish.Dan Med J. 2020 Jul 1;67(7):A11190617. Dan Med J. 2020. PMID: 32734886
-
Tensor tenopexy: a clinical study to assess its effectiveness in improving Eustachian tube function and preventing hearing loss in patients with cleft palate.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013 Sep;66(9):e239-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 Jun 1. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2013. PMID: 23732073 Clinical Trial.
-
The role of the tensor veli palatini muscle in the development of cleft palate-associated middle ear problems.Clin Oral Investig. 2016 Sep;20(7):1389-401. doi: 10.1007/s00784-016-1828-x. Epub 2016 May 7. Clin Oral Investig. 2016. PMID: 27153847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous