Network pharmacology-based dissection of the underlying mechanisms of dyspnoea induced by zedoary turmeric oil
- PMID: 35318816
- PMCID: PMC9313566
- DOI: 10.1111/bcpt.13722
Network pharmacology-based dissection of the underlying mechanisms of dyspnoea induced by zedoary turmeric oil
Abstract
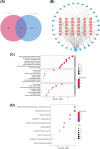
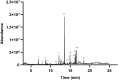
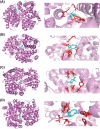
Zedoary turmeric oil (ZTO) has been widely used in clinic. However, the unpleasant induced dyspnoea inevitably impedes its clinical application. Thus, it is urgent to elucidate the mechanism underlying the ZTO-induced dyspnoea. In this study, network pharmacology was firstly performed to search the clue of ZTO-induced dyspnoea. The key target genes of ZTO-induced dyspnoea were analysed using GO enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis. GO analysis suggested that haem binding could be a key molecular function involved in ZTO-induced dyspnoea. Hence, the haemoglobin (Hb) was focused for its oxygen-carrying capacity with haem as its critical component binding to the oxygen. Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrum indicated that the ZTO injection (ZTOI) perturbed the Soret band of Hb, suggesting an interaction between ZTO and Hb. GC-MS analysis revealed that β-elemene, germacrone, curdione and furanodiene were main components of ZTOI. Molecular docking was used to illustrate the high affinity between representative sesquiterpenes and Hb, which was finally confirmed by surface plasmon resonance, suggesting their potential roles in dyspnoea by ZTO. Following a network pharmacology-driven strategy, our study revealed an intervened Hb-based mechanism underlying the ZTO-induced dyspnoea, providing a reference for elucidating mechanism underlying adverse drug reactions of herbal medicines in clinic.
Keywords: binding affinity; dyspnoea; haemoglobin; network pharmacology; zedoary turmeric oil.
© 2022 The Authors. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Association for the Publication of BCPT (former Nordic Pharmacological Society).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
β-Elemene in zedoary turmeric oil injection induces dyspnea by binding to hemoglobin and upregulating HIF-1α.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Mar 1;321:117531. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117531. Epub 2023 Nov 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38042387
-
Multiple anti-inflammatory mechanisms of Zedoary Turmeric Oil Injection against lipopolysaccharides-induced acute lung injury in rats elucidated by network pharmacology combined with transcriptomics.Phytomedicine. 2022 Nov;106:154418. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154418. Epub 2022 Aug 31. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36099655
-
[Study on the Fingerprint of Kingkong Zedoary Turmeric Oil].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;36(6):744-8. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27491236 Chinese.
-
Applications of nanoparticles in herbal medicine: zedoary turmeric oil and its active compound β-elemene.Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(6):1093-102. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X11009421. Am J Chin Med. 2011. PMID: 22083983 Review.
-
Analysis on internal mechanism of zedoary turmeric in treatment of liver cancer based on pharmacodynamic substances and pharmacodynamic groups.Chin Herb Med. 2022 Sep 27;14(4):479-493. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.06.007. eCollection 2022 Oct. Chin Herb Med. 2022. PMID: 36405057 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumae Rhizoma: A botanical drug against infectious diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1015098. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1015098. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36703758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shikonin Suppresses Cell Tumorigenesis in Gastric Cancer Associated with the Inhibition of c-Myc and Yap-1.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(13):1919-1929. doi: 10.2174/0113862073254088231020082912. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37957853
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

