Unique Clinical, Immune, and Genetic Signature in Patients with Borrelial Meningoradiculoneuritis1
- PMID: 35318928
- PMCID: PMC8962912
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2804.211831
Unique Clinical, Immune, and Genetic Signature in Patients with Borrelial Meningoradiculoneuritis1
Abstract
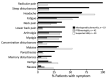
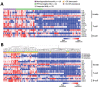
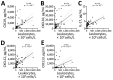
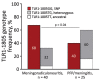
Lyme neuroborreliosis (LNB) in Europe may manifest with painful meningoradiculoneuritis (also known as Bannwarth syndrome) or lymphocytic meningitis with or without cranial neuritis (peripheral facial palsy). We assessed host immune responses and the prevalence of TLR1 (toll-like receptor 1)-1805GG polymorphism to gain insights into the pathophysiology of these conditions. Regardless of LNB manifestation, most mediators associated with innate and adaptive immune responses were concentrated in cerebrospinal fluid; serum levels were unremarkable. When stratified by specific clinical manifestation, patients with meningoradiculoneuritis had higher levels of B-cell chemoattractants CXC motif chemokine ligand (CXCL) 12 and CXCL13 and T-cell-associated mediators CXCL9, CXCL10, and interleukin 17, compared with those without radicular pain. Moreover, these patients had a higher frequency of TLR1-1805GG polymorphism and more constitutional symptoms. These findings demonstrate that meningoradiculoneuritis is a distinct clinical entity with unique immune and genetic pathophysiology, providing new considerations for the study of LNB and borrelial meningoradiculitis.
Keywords: Lyme disease; Slovenia; United States; bacteria; cytokines; genetics; immune response; inflammation; meningitis/encephalitis; meningoradiculoneuritis; neuroborreliosis; peripheral facial palsy; polymorphism; vector-borne infections.
Figures


References
-
- Mygland A, Ljostad U, Fingerle V, Rupprecht T, Schmutzhard E, Steiner I. EFNS guidelines on the diagnosis and management of European Lyme neuroborreliosis. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:8–16, e1–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

