Quercetin Reduces the Virulence of S. aureus by Targeting ClpP to Protect Mice from MRSA-Induced Lethal Pneumonia
- PMID: 35319277
- PMCID: PMC9045277
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.02340-21
Quercetin Reduces the Virulence of S. aureus by Targeting ClpP to Protect Mice from MRSA-Induced Lethal Pneumonia
Abstract
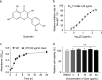
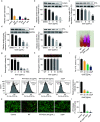
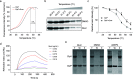
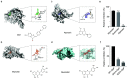
The dramatic increase of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) poses a great challenge to the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infections. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify novel anti-infective agents to attack new targets to overcome antibiotic resistance. Casein hydrolase P (ClpP) is a key virulence factor in S. aureus to maintain cellular homeostasis. We screened from flavonoids and finally determined that quercetin could effectively attenuate the virulence of MRSA. The results of the thermal shift assay showed that quercetin could bind to ClpP and reduce the thermal stability of ClpP, and the KD value between quercetin and ClpP was 197 nM as determined by localized surface plasmon resonance. We found that quercetin exhibited a protective role of a mouse model of MRSA-induced lethal infection in a murine model. Based on the above facts, quercetin, as a ClpP inhibitor, could be further developed as a potential candidate for antivirulence agents to combat S. aureus infections. IMPORTANCE The resistance of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) to various antibiotics has increased dramatically, and thus the development of new anti-infective drugs with new targets is urgently needed to combat resistance. Caseinolytic peptidase P (ClpP) is a casein hydrolase that has been shown to regulate a variety of important virulence factors in S. aureus. Here, we found that quercetin, a small-molecule compound from traditional Chinese herbal flavonoids, effectively inhibits ClpP activity. Quercetin attenuates the expression of multiple virulence factors in S. aureus and effectively protects mice from lethal pneumonia caused by MRSA. In conclusion, we determined that quercetin is a ClpP inhibitor and an effective lead compound for the development of a virulence factor-based treatment for S. aureus infection.
Keywords: MRSA; antivirulence; caseinolytic peptidase P; inhibitor; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nepetin reduces virulence factors expression by targeting ClpP against MRSA-induced pneumonia infection.Virulence. 2022 Dec;13(1):578-588. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2051313. Virulence. 2022. PMID: 35363605 Free PMC article.
-
Ayanin, a natural flavonoid inhibitor of Caseinolytic protease, is a promising therapeutic agent to combat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115814. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115814. Epub 2023 Sep 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37769713
-
Sesamin targets ClpP which attenuates virulence of S. aureus and protects mice from fatal pneumonia induced by MRSA.J Appl Microbiol. 2025 Feb 3;136(2):lxaf003. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxaf003. J Appl Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39805732
-
Tamarixetin Attenuated the Virulence of Staphylococcus aureus by Directly Targeting Caseinolytic Protease P.J Nat Prod. 2022 Aug 26;85(8):1936-1944. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00138. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Nat Prod. 2022. PMID: 35833867 Review.
-
Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 17;10:107. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00107. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32257966 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thwarting resistance: MgrA inhibition with methylophiopogonanone a unveils a new battlefront against S. aureus.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024 Feb 27;10(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41522-024-00485-w. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2024. PMID: 38413623 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the potential of isorhapontigenin in targeting the MgrA regulatory network: a paradigm shift for attenuating MRSA virulence.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Sep 4;68(9):e0061124. doi: 10.1128/aac.00611-24. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 39046236 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the molecular interactions between urease subunit gamma from MRSA and drugs: an integrative approach by STD-NMR and molecular docking studies.RSC Adv. 2024 Oct 1;14(42):30859-30872. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01732c. eCollection 2024 Sep 24. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39355333 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm and Antihemolytic Activities of Actinostemma lobatum Extract Rich in Quercetin against Staphylococcus aureus.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):1075. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081075. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204420 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen-Containing Flavonoids-Preparation and Biological Activity.ACS Omega. 2024 Jul 29;9(32):34938-34950. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04627. eCollection 2024 Aug 13. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39157108 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laxminarayan R, Duse A, Wattal C, Zaidi AK, Wertheim HF, Sumpradit N, Vlieghe E, Hara GL, Gould IM, Goossens H, Greko C, So AD, Bigdeli M, Tomson G, Woodhouse W, Ombaka E, Peralta AQ, Qamar FN, Mir F, Kariuki S, Bhutta ZA, Coates A, Bergstrom R, Wright GD, Brown ED, Cars O. 2013. Antibiotic resistance-the need for global solutions. Lancet Infect Dis 13:1057–1098. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70318-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lehar SM, Pillow T, Xu M, Staben L, Kajihara KK, Vandlen R, DePalatis L, Raab H, Hazenbos WL, Morisaki JH, Kim J, Park S, Darwish M, Lee BC, Hernandez H, Loyet KM, Lupardus P, Fong R, Yan D, Chalouni C, Luis E, Khalfin Y, Plise E, Cheong J, Lyssikatos JP, Strandh M, Koefoed K, Andersen PS, Flygare JA, Wah Tan M, Brown EJ, Mariathasan S. 2015. Novel antibody-antibiotic conjugate eliminates intracellular S. aureus. Nature 527:323–328. doi:10.1038/nature16057. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

