Feasibility, Enjoyment, and Language Comprehension Impact of a Tablet- and GameFlow-Based Story-Listening Game for Kindergarteners: Methodological and Mixed Methods Study
- PMID: 35319480
- PMCID: PMC8987971
- DOI: 10.2196/34698
Feasibility, Enjoyment, and Language Comprehension Impact of a Tablet- and GameFlow-Based Story-Listening Game for Kindergarteners: Methodological and Mixed Methods Study
Abstract
Background: Enjoyment plays a key role in the success and feasibility of serious gaming interventions. Unenjoyable games will not be played, and in the case of serious gaming, learning will not occur. Therefore, a so-called GameFlow model has been developed, which intends to guide (serious) game developers in the process of creating and evaluating enjoyment in digital (serious) games. Regarding language learning, a variety of serious games targeting specific language components exist in the market, albeit often without available assessments of enjoyment or feasibility.
Objective: This study evaluates the enjoyment and feasibility of a tablet-based, serious story-listening game for kindergarteners, developed based on the principles of the GameFlow model. This study also preliminarily explores the possibility of using the game to foster language comprehension.
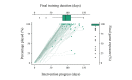
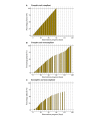
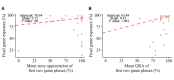
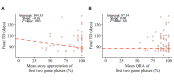
Methods: Within the framework of a broader preventive reading intervention, 91 kindergarteners aged 5 years with a cognitive risk for dyslexia were asked to play the story game for 12 weeks, 6 days per week, either combined with a tablet-based phonics intervention or control games. The story game involved listening to and rating stories and responding to content-related questions. Game enjoyment was assessed through postintervention questionnaires, a GameFlow-based evaluation, and in-game story rating data. Feasibility was determined based on in-game general question response accuracy (QRA), reflecting the difficulty level, attrition rate, and final game exposure and training duration. Moreover, to investigate whether game enjoyment and difficulty influenced feasibility, final game exposure and training duration were predicted based on the in-game initial story ratings and initial QRA. Possible growth in language comprehension was explored by analyzing in-game QRA as a function of the game phase and baseline language skills.
Results: Eventually, data from 82 participants were analyzed. The questionnaire and in-game data suggested an overall enjoyable game experience. However, the GameFlow-based evaluation implied room for game design improvement. The general QRA confirmed a well-adapted level of difficulty for the target sample. Moreover, despite the overall attrition rate of 39% (32/82), 90% (74/82) of the participants still completed 80% of the game, albeit with a large variation in training days. Higher initial QRA significantly increased game exposure (β=.35; P<.001), and lower initial story ratings significantly slackened the training duration (β=-0.16; P=.003). In-game QRA was positively predicted by game phase (β=1.44; P=.004), baseline listening comprehension (β=1.56; P=.002), and vocabulary (β=.16; P=.01), with larger QRA growth over game phases in children with lower baseline listening comprehension skills (β=-0.08; P=.04).
Conclusions: Generally, the story game seemed enjoyable and feasible. However, the GameFlow model evaluation and predictive relationships imply room for further game design improvements. Furthermore, our results cautiously suggest the potential of the game to foster language comprehension; however, future randomized controlled trials should further elucidate the impact on language comprehension.
Keywords: GameFlow; enjoyment; feasibility; language comprehension; serious gaming.
©Femke Vanden Bempt, Maria Economou, Ward Dehairs, Maaike Vandermosten, Jan Wouters, Pol Ghesquière, Jolijn Vanderauwera. Originally published in JMIR Serious Games (https://games.jmir.org), 23.03.2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relationship Between Children's Enjoyment, User Experience Satisfaction, and Learning in a Serious Video Game for Nutrition Education: Empirical Pilot Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2020 Sep 17;8(3):e21813. doi: 10.2196/21813. JMIR Serious Games. 2020. PMID: 32940609 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of inference-making in children using comprehension questions and story retelling: Effect of text modality and a story presentation format.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021 May;56(3):637-652. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.12620. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2021. PMID: 34028960
-
Assessing the Noninferiority of a Rhythm and Language Training Serious Game Combined With Speech Therapy Versus Speech Therapy Care for Children With Dyslexia: Protocol for an Investigator-Blinded Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 Apr 3;14:e71326. doi: 10.2196/71326. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40179385 Free PMC article.
-
Phonics training for English-speaking poor readers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Nov 14;11(11):CD009115. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009115.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30480759 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Serious Games as a Therapeutic Tool in Pediatric Urology: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions.Int Neurourol J. 2024 Sep;28(3):185-195. doi: 10.5213/inj.2448322.161. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Int Neurourol J. 2024. PMID: 39363409 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical Structure in Pre-Readers at Cognitive Risk for Dyslexia: Baseline Differences and Response to Intervention.Neurobiol Lang (Camb). 2024 Jun 3;5(2):264-287. doi: 10.1162/nol_a_00122. eCollection 2024. Neurobiol Lang (Camb). 2024. PMID: 38832361 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of a Novel Video Game on Young Soccer Players' Sports Performance and Attention: Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Serious Games. 2024 May 27;12:e52275. doi: 10.2196/52275. JMIR Serious Games. 2024. PMID: 38801708 Free PMC article.
-
Speech perception deficits and the effect of envelope-enhanced story listening combined with phonics intervention in pre-readers at risk for dyslexia.Front Psychol. 2022 Oct 28;13:1021767. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1021767. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36389538 Free PMC article.
-
Neural synchronization and intervention in pre-readers who later on develop dyslexia.Eur J Neurosci. 2023 Feb;57(3):547-567. doi: 10.1111/ejn.15894. Epub 2022 Dec 23. Eur J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36518008 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Montero G, Gomez J. Serious games in special education. A practitioner's experience review. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Entertainment Computing; ICEC '18; September 18-20, 2018; Poznan, Poland. 2018. pp. 397–401. - DOI
-
- Dörner R, Göbel S, Effelsberg W, Wiemeyer J. Serious games: foundations, concepts and practice. Cham, The Netherlands: Springer; 2016. pp. 2–3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

