Functional and Structural Development of Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses
- PMID: 35319739
- PMCID: PMC8963661
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.63.3.21
Functional and Structural Development of Mouse Cone Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses
Abstract
Purpose: Cone photoreceptors of the retina use a sophisticated ribbon-containing synapse to convert light-dependent changes in membrane potential into release of synaptic vesicles (SVs). We aimed to study the functional and structural maturation of mouse cone photoreceptor ribbon synapses during postnatal development and to investigate the role of the synaptic ribbon in SV release.
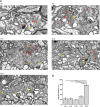
Methods: We performed patch-clamp recordings from cone photoreceptors and their postsynaptic partners, the horizontal cells during postnatal retinal development to reveal the functional parameters of the synapses. To investigate the occurring structural changes, we applied immunocytochemistry and electron microscopy.
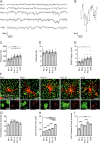
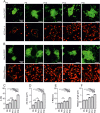
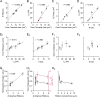
Results: We found that immature cone photoreceptor terminals were smaller, they had fewer active zones (AZs) and AZ-anchored synaptic ribbons, and they produced a smaller Ca2+ current than mature photoreceptors. The number of postsynaptic horizontal cell contacts to synaptic terminals increased with age. However, tonic and spontaneous SV release at synaptic terminals stayed similar during postnatal development. Multiquantal SV release was present in all age groups, but mature synapses produced larger multiquantal events than immature ones. Remarkably, at single AZs, tonic SV release was attenuated during maturation and showed an inverse relationship with the appearance of anchored synaptic ribbons.
Conclusions: Our developmental study suggests that the presence of synaptic ribbons at the AZs attenuates tonic SV release and amplifies multiquantal SV release. However, spontaneous SV release may not depend on the presence of synaptic ribbons or voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels at the AZs.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synaptic vesicle release during ribbon synapse formation of cone photoreceptors.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Nov 4;16:1022419. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1022419. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36406751 Free PMC article.
-
Signal transmission at invaginating cone photoreceptor synaptic contacts following deletion of the presynaptic cytomatrix protein Bassoon in mouse retina.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019 Jun;226(2):e13241. doi: 10.1111/apha.13241. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30554473
-
Functional Roles of Complexin 3 and Complexin 4 at Mouse Photoreceptor Ribbon Synapses.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 22;36(25):6651-67. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4335-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27335398 Free PMC article.
-
The dynamic architecture of photoreceptor ribbon synapses: cytoskeletal, extracellular matrix, and intramembrane proteins.Vis Neurosci. 2011 Nov;28(6):453-71. doi: 10.1017/S0952523811000356. Vis Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22192503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic [Ca(2+)] and GCAPs: aspects on the structure and function of photoreceptor ribbon synapses.Front Mol Neurosci. 2014 Feb 6;7:3. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00003. eCollection 2014. Front Mol Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24567702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light-dependent regulation of neurotransmitter release from rod photoreceptor ribbon synapses involves an interplay of Complexin 4 and Transducin with the SNARE complex.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Feb 28;17:1308466. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1308466. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38481472 Free PMC article.
-
Functional maturation of the rod bipolar to AII-amacrine cell ribbon synapse in the mouse retina.Cell Rep. 2023 Nov 28;42(11):113440. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113440. Epub 2023 Nov 16. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37976158 Free PMC article.
-
The first synapse in vision in the aging mouse retina.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 3;17:1291054. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1291054. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38026697 Free PMC article.
-
GRF2 Is Crucial for Cone Photoreceptor Viability and Ribbon Synapse Formation in the Mouse Retina.Cells. 2023 Nov 4;12(21):2574. doi: 10.3390/cells12212574. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37947653 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptic vesicle release during ribbon synapse formation of cone photoreceptors.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Nov 4;16:1022419. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1022419. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36406751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feigenspan A, Babai N.. Functional properties of spontaneous excitatory currents and encoding of light/dark transitions in horizontal cells of the mouse retina. Eur J Neurosci. 2015; 42: 2615–2632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

