Sacral neuromodulation of bladder underactivity induced by prolonged pudendal afferent firing in cats
- PMID: 35319898
- PMCID: PMC9076414
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00012.2022
Sacral neuromodulation of bladder underactivity induced by prolonged pudendal afferent firing in cats
Abstract
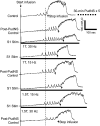
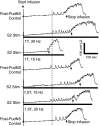
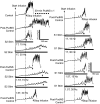
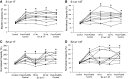
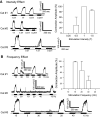
This study examined the effect of sacral neuromodulation on persistent bladder underactivity induced by prolonged pudendal nerve stimulation (PudNS). In 10 α-chloralose-anesthetized cats, repetitive application of 30-min PudNS induced bladder underactivity evident as an increase in bladder capacity during a cystometrogram (CMG). S1 or S2 dorsal root stimulation (15 or 30 Hz) at 1 or 1.5 times threshold intensity (T) for inducing reflex hindlimb movement (S1) or anal sphincter twitch (S2) was applied during a CMG to determine if the stimulation can reverse the bladder underactivity. Persistent (>3 h) bladder underactivity consisting of a significant increase in bladder capacity to 163.1 ± 11.3% of control was induced after repetitive (1-10 times) application of 30-min PudNS. S2 but not S1 dorsal root stimulation at 15 Hz and 1 T intensity reversed the PudNS-induced bladder underactivity by significantly reducing the large bladder capacity to 124.3 ± 12.9% of control. Other stimulation parameters were not effective. After the induction of persistent underactivity, recordings of reflex bladder activity under isovolumetric conditions revealed that S2 dorsal root stimulation consistently induced the largest bladder contraction at 15 Hz and 1 T when compared with other frequencies (5-40 Hz) or intensities (0.25-1.5 T). This study provides basic science evidence consistent with the hypothesis that abnormal pudendal afferent activity contributes to the bladder underactivity in Fowler's syndrome and that sacral neuromodulation treats this disorder by reversing the bladder inhibition induced by pudendal nerve afferent activity.
Keywords: bladder; neuromodulation; pudendal; sacral; underactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Jonas U, Fowler CJ, Chancellor MB, Elhilali MM, Fall M, Gajewski JB, Grünewald V, Hassouna MM, Hombergh UVD, Janknegt R, van Kerrebroeck PEV, Lylcklama À Nijeholt AAB, Siegel SW, Schmidt RA. Efficacy of sacral nerve stimulation for urinary retention: results 18 months after implantation. J Urol 165: 15–19, 2001. doi: 10.1097/00005392-200101000-00004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- van Kerrebroeck PEV, van Voskuilen AC, Heesakkers JPFA, Lycklama Á Nijholt AAB, Siegel S, Jonas U, Fowler CJ, Fall M, Gajewski JB, Hassouna MM, Cappellano F, Elhilali MM, Milam DF, Das AK, Dijkema HE, van den Hombergh U, Dijkema HE, van den Hombergh U. Results of sacral neuromodulation therapy for urinary voiding dysfunction: outcomes of a prospective, worldwide clinical study. J Urol 178: 2029–2034, 2007. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2007.07.032. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

