Somatostatin venom analogs evolved by fish-hunting cone snails: From prey capture behavior to identifying drug leads
- PMID: 35319982
- PMCID: PMC8942377
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abk1410
Somatostatin venom analogs evolved by fish-hunting cone snails: From prey capture behavior to identifying drug leads
Abstract
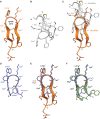
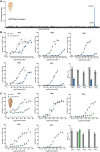
Somatostatin (SS) is a peptide hormone with diverse physiological roles. By investigating a deep-water clade of fish-hunting cone snails, we show that predator-prey evolution has generated a diverse set of SS analogs, each optimized to elicit specific systemic physiological effects in prey. The increased metabolic stability, distinct SS receptor activation profiles, and chemical diversity of the venom analogs make them suitable leads for therapeutic application, including pain, cancer, and endocrine disorders. Our findings not only establish the existence of SS-like peptides in animal venoms but also serve as a model for the synergy gained from combining molecular phylogenetics and behavioral observations to optimize the discovery of natural products with biomedical potential.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Fish-hunting cone snail venoms are a rich source of minimized ligands of the vertebrate insulin receptor.Elife. 2019 Feb 12;8:e41574. doi: 10.7554/eLife.41574. Elife. 2019. PMID: 30747102 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the origins of fish hunting in venomous cone snails from studies of Conus tessulatus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 21;112(16):5087-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424435112. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25848010 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized insulin is used for chemical warfare by fish-hunting cone snails.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Feb 10;112(6):1743-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423857112. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25605914 Free PMC article.
-
Predatory and Defensive Strategies in Cone Snails.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;16(2):94. doi: 10.3390/toxins16020094. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38393171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prey-Capture Strategies of Fish-Hunting Cone Snails: Behavior, Neurobiology and Evolution.Brain Behav Evol. 2015 Sep;86(1):58-74. doi: 10.1159/000438449. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Brain Behav Evol. 2015. PMID: 26397110 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of the venom of Conus flavidus from Red Sea reveals potential pharmacological applications.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024 Jun;22(2):100375. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2024.100375. Epub 2024 Apr 27. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38797555 Free PMC article.
-
A previously unrecognized superfamily of macro-conotoxins includes an inhibitor of the sensory neuron calcium channel Cav2.3.PLoS Biol. 2023 Aug 3;21(8):e3002217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002217. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37535677 Free PMC article.
-
An N-Terminally Elongated Peptide From Conus rolani Defines a New Class of Ribbon α-Conotoxins Targeting Muscle nAChRs.FASEB J. 2025 Jun 30;39(12):e70698. doi: 10.1096/fj.202500721RR. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 40536237 Free PMC article.
-
A toxin-based approach to neuropeptide and peptide hormone discovery.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Aug 31;16:1176662. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1176662. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37720554 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca).Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 26;23(7):266. doi: 10.3390/md23070266. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40710491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- King G. F., Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 11, 1469–1484 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Yarotskyy V., Elmslie K. S., Omega-conotoxin GVIA alters gating charge movement of N-type (CaV2.2) calcium channels. J. Neurophysiol. 101, 332–340 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Miljanich G. P., Ziconotide: Neuronal calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 11, 3029–3040 (2004). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

