Relaxation time asymmetry in stator dynamics of the bacterial flagellar motor
- PMID: 35319986
- PMCID: PMC8942351
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl8112
Relaxation time asymmetry in stator dynamics of the bacterial flagellar motor
Abstract
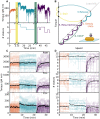
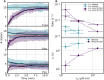
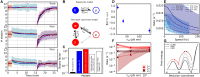
The bacterial flagellar motor is the membrane-embedded rotary motor, which turns the flagellum that provides thrust to many bacteria. This large multimeric complex, composed of a few dozen constituent proteins, is a hallmark of dynamic subunit exchange. The stator units are inner-membrane ion channels that dynamically bind to the peptidoglycan at the rotor periphery and apply torque. Their dynamic exchange is a function of the viscous load on the flagellum, allowing the bacterium to adapt to its local environment, although the molecular mechanisms of mechanosensitivity remain unknown. Here, by actively perturbing the steady-state stator stoichiometry of individual motors, we reveal a stoichiometry-dependent asymmetry in stator remodeling kinetics. We interrogate the potential effect of next-neighbor interactions and local stator unit depletion and find that neither can explain the observed asymmetry. We then simulate and fit two mechanistically diverse models that recapitulate the asymmetry, finding assembly dynamics to be particularly well described by a two-state catch-bond mechanism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 22;14(12):1488. doi: 10.3390/biom14121488. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Chaperone for the Stator Units of a Bacterial Flagellum.mBio. 2019 Aug 6;10(4):e01732-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01732-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31387912 Free PMC article.
-
Catch bond drives stator mechanosensitivity in the bacterial flagellar motor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Dec 5;114(49):12952-12957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1716002114. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 29183968 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the MotA(M206I) Mutation on Torque Generation and Stator Assembly in the Salmonella H+-Driven Flagellar Motor.J Bacteriol. 2019 Feb 25;201(6):e00727-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00727-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30642987 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of torque generation in the bi-directional bacterial flagellar motor.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Feb;47(2):160-172. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 34294545 Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring Bacterial Flagellar Motor Dynamics via a Bead Assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2881:43-64. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4280-1_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39704937
-
A multi-state dynamic process confers mechano-adaptation to a biological nanomachine.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 10;13(1):5327. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33075-5. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36088344 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Dynamics of the Bacterial Flagellar Motor Complex.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 22;14(12):1488. doi: 10.3390/biom14121488. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39766194 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tusk S. E., Delalez N. J., Berry R. M., Subunit exchange in protein complexes. J. Mol. Biol. 430, 4557–4579 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Leake M. C., Chandler J. H., Wadhams G. H., Bai F., Berry R. M., Armitage J. P., Stoichiometry and turnover in single, functioning membrane protein complexes. Nature 443, 355–358 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

