KCNQ2 and KCNQ5 form heteromeric channels independent of KCNQ3
- PMID: 35320039
- PMCID: PMC9060518
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2117640119
KCNQ2 and KCNQ5 form heteromeric channels independent of KCNQ3
Abstract
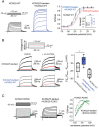
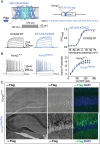
KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 channels are associated with multiple neurodevelopmental disorders and are also therapeutic targets for neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. For more than two decades, it has been thought that most KCNQ channels in the brain are either KCNQ2/3 or KCNQ3/5 heteromers. Here, we investigated the potential heteromeric compositions of KCNQ2-containing channels. We applied split-intein protein trans-splicing to form KCNQ2/5 tandems and coexpressed these with and without KCNQ3. Unexpectedly, we found that KCNQ2/5 tandems form functional channels independent of KCNQ3 in heterologous cells. Using mass spectrometry, we went on to demonstrate that KCNQ2 associates with KCNQ5 in native channels in the brain, even in the absence of KCNQ3. Additionally, our functional heterologous expression data are consistent with the formation of KCNQ2/3/5 heteromers. Thus, the composition of KCNQ channels is more diverse than has been previously recognized, necessitating a re-examination of the genotype/phenotype relationship of KCNQ2 pathogenic variants.
Keywords: KCNQ2; KCNQ3; KCNQ5; autism; epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heteromeric Assembly of Truncated Neuronal Kv7 Channels: Implications for Neurologic Disease and Pharmacotherapy.Mol Pharmacol. 2020 Sep;98(3):192-202. doi: 10.1124/mol.120.119644. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32580997
-
Conditional deletions of epilepsy-associated KCNQ2 and KCNQ3 channels from cerebral cortex cause differential effects on neuronal excitability.J Neurosci. 2014 Apr 9;34(15):5311-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3919-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24719109 Free PMC article.
-
The Amyloid Precursor Protein C99 Fragment Modulates Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021 Jul 28;55(S3):157-170. doi: 10.33594/000000397. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34318654 Free PMC article.
-
Made for "anchorin": Kv7.2/7.3 (KCNQ2/KCNQ3) channels and the modulation of neuronal excitability in vertebrate axons.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011 Apr;22(2):185-92. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.10.001. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 20940059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flexible Stoichiometry: Implications for KCNQ2- and KCNQ3-Associated Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Dev Neurosci. 2021;43(3-4):191-200. doi: 10.1159/000515495. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Dev Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33794528 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel KCNQ2 missense variant expands the genotype spectrum of DEE7.Neurol Sci. 2024 Nov;45(11):5481-5488. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07655-w. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Neurol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38880853
-
Kv Channel Ancillary Subunits: Where Do We Go from Here?Physiology (Bethesda). 2022 Sep 1;37(5):0. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00005.2022. Physiology (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35797055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kv7 channel opener retigabine reduces self-administration of cocaine but not sucrose in rats.Addict Biol. 2024 Aug;29(8):e13428. doi: 10.1111/adb.13428. Addict Biol. 2024. PMID: 39087789 Free PMC article.
-
Glial KCNQ K+ channels control neuronal output by regulating GABA release from glia in C. elegans.Neuron. 2024 Jun 5;112(11):1832-1847.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2024.02.013. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Neuron. 2024. PMID: 38460523 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate activation mechanism of human KCNQ5.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Apr 8;122(14):e2416738122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2416738122. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40172963
References
-
- Nappi P., et al. , Epileptic channelopathies caused by neuronal Kv7 (KCNQ) channel dysfunction. Pflugers Arch. 472, 881–898 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Sands T. T., et al. , Autism and developmental disability caused by KCNQ3 gain-of-function variants. Ann. Neurol. 86, 181–192 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Delmas P., Brown D. A., Pathways modulating neural KCNQ/M (Kv7) potassium channels. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 850–862 (2005). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

