Multi-Modal Imaging Genetics Data Fusion via a Hypergraph-Based Manifold Regularization: Application to Schizophrenia Study
- PMID: 35320094
- PMCID: PMC9661879
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2022.3161828
Multi-Modal Imaging Genetics Data Fusion via a Hypergraph-Based Manifold Regularization: Application to Schizophrenia Study
Abstract
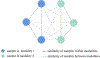
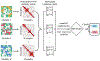
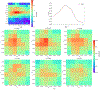
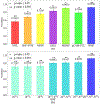
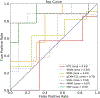
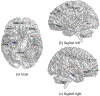
Recent studies show that multi-modal data fusion techniques combine information from diverse sources for comprehensive diagnosis and prognosis of complex brain disorder, often resulting in improved accuracy compared to single-modality approaches. However, many existing data fusion methods extract features from homogeneous networs, ignoring heterogeneous structural information among multiple modalities. To this end, we propose a Hypergraph-based Multi-modal data Fusion algorithm, namely HMF. Specifically, we first generate a hypergraph similarity matrix to represent the high-order relationships among subjects, and then enforce the regularization term based upon both the inter- and intra-modality relationships of the subjects. Finally, we apply HMF to integrate imaging and genetics datasets. Validation of the proposed method is performed on both synthetic data and real samples from schizophrenia study. Results show that our algorithm outperforms several competing methods, and reveals significant interactions among risk genes, environmental factors and abnormal brain regions.
Figures

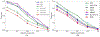
Similar articles
-
Hypergraph-regularized multimodal learning by graph diffusion for imaging genetics based Alzheimer's Disease diagnosis.Med Image Anal. 2023 Oct;89:102883. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102883. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Med Image Anal. 2023. PMID: 37467641
-
Detection of relationships among multi-modal brain imaging meta-features via information flow.J Neurosci Methods. 2018 Jan 15;294:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2017.11.006. Epub 2017 Nov 14. J Neurosci Methods. 2018. PMID: 29146193
-
Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using hypergraph p-Laplacian regularized multi-task feature learning.J Biomed Inform. 2023 Apr;140:104326. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2023.104326. Epub 2023 Mar 3. J Biomed Inform. 2023. PMID: 36870585
-
Multi-modal neuroimaging feature selection with consistent metric constraint for diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Med Image Anal. 2020 Feb;60:101625. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101625. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Med Image Anal. 2020. PMID: 31841947 Free PMC article.
-
A Method for Multimodal IVA Fusion Within a MISA Unified Model Reveals Markers of Age, Sex, Cognition, and Schizophrenia in Large Neuroimaging Studies.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Dec 1;45(17):e70037. doi: 10.1002/hbm.70037. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 39560198 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identifiability in Functional Connectivity May Unintentionally Inflate Prediction Results.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 2:arXiv:2308.01451v1. ArXiv. 2023. PMID: 37576121 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Neuroimage Analysis Methods and Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Reliable Biomarkers and Accurate Diagnosis of Schizophrenia: Achievements Made by Chinese Scholars Around the Past Decade.Schizophr Bull. 2025 Mar 14;51(2):325-342. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbae110. Schizophr Bull. 2025. PMID: 38982882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in Gray Matter Structure Linked to Frequency-Specific Cortico-Subcortical Connectivity in Schizophrenia via Multimodal Data Fusion.Neuroinformatics. 2025 Apr 26;23(2):31. doi: 10.1007/s12021-025-09728-3. Neuroinformatics. 2025. PMID: 40285903
References
-
- Lahat D, Adali T and Jutten C, “Multimodal Data Fusion: An Overview of Methods, Challenges, and Prospects,”Proceedings of the IEEE, vol. 103, no. 9, pp. 1449–1477, Sept. 2015.
-
- Li Y, Yang M and Zhang Z, “A Survey of Multi-View Representation Learning,” IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, vol. 31, no. 10, pp. 1863–1883, 1 Oct. 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

