Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 induces cell competition
- PMID: 35320322
- PMCID: PMC8979454
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010431
Human papillomavirus type 16 E6 induces cell competition
Abstract
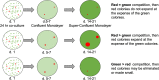
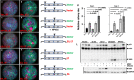
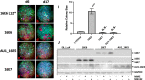
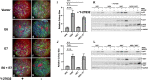
High-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infections induce squamous epithelial tumors in which the virus replicates. Initially, the virus-infected cells are untransformed, but expand in both number and area at the expense of uninfected squamous epithelial cells. We have developed an in vitro assay in which colonies of post-confluent HPV16 expressing cells outcompete and displace confluent surrounding uninfected keratinocytes. The enhanced colony competition induced by the complete HPV16 genome is conferred by E6 expression alone, not by individual expression of E5 or E7, and requires E6 interaction with p53. E6-expressing keratinocytes undermine and displace adjacent normal keratinocytes from contact with the attachment substrate, thereby expanding the area of the E6-expressing colony at the expense of normal keratinocytes. These new results separate classic oncogenicity that is primarily conferred by HPV16 E7 from cell competition that we show is primarily conferred by E6 and provides a new biological role for E6 oncoproteins from high-risk human papillomaviruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Knipe D, Howley PM. Virology. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2007. p. 1662.
-
- Brandsma JL, Yang ZH, Barthold SW, Johnson EA. Use of a rapid, efficient inoculation method to induce papillomas by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus DNA shows that the E7 gene is required. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88(11):4816–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4816 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC51757. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu X, Xiao W, Brandsma JL. Papilloma formation by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus requires E1 and E2 regulatory genes in addition to E6 and E7 transforming genes. J Virol. 1994;68(9):6097–102. Epub 1994/09/01. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.9.6097-6102.1994 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC237021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

