Epigenetic and Transcriptional Regulation of Innate Immunity in Cancer
- PMID: 35320354
- PMCID: PMC9177721
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-3503
Epigenetic and Transcriptional Regulation of Innate Immunity in Cancer
Abstract
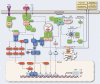
Innate immune cells participate in the detection of tumor cells via complex signaling pathways mediated by pattern-recognition receptors, such as Toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding and oligomerization domain-like receptors. These pathways are finely tuned via multiple mechanisms, including epigenetic regulation. It is well established that hematopoietic progenitors generate innate immune cells that can regulate cancer cell behavior, and the disruption of normal hematopoiesis in pathologic states may lead to altered immunity and the development of cancer. In this review, we discuss the epigenetic and transcriptional mechanisms that underlie the initiation and amplification of innate immune signaling in cancer. We also discuss new targeting possibilities for cancer control that exploit innate immune cells and signaling molecules, potentially heralding the next generation of immunotherapy.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in innate immune responses.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013 Apr;1283:67-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06786.x. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013. PMID: 23163321 Review.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms Regulate Innate Immunity against Uropathogenic and Commensal-Like Escherichia coli in the Surrogate Insect Model Galleria mellonella.Infect Immun. 2017 Sep 20;85(10):e00336-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00336-17. Print 2017 Oct. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28739824 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and pathways of innate immune activation and regulation in health and cancer.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014;10(11):3270-85. doi: 10.4161/21645515.2014.979640. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2014. PMID: 25625930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics and innate immunity: the 'unTolld' story.Immunol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;94(7):631-9. doi: 10.1038/icb.2016.24. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26924642 Review.
-
Toll-Like Receptors in Cystic Fibrosis: Impact of Dysfunctional microRNA on Innate Immune Responses in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung.J Innate Immun. 2016;8(6):541-549. doi: 10.1159/000444687. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Innate Immun. 2016. PMID: 27043239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular genetic characteristics of thymic epithelial tumors with distinct histological subtypes.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(9):10575-10586. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5795. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36916520 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Proteomic Analyses of Proinflammatory Cytokines in a Mouse Model of Liver Transplant Rejection.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 12;2022:5188584. doi: 10.1155/2022/5188584. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35993024 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Role of Mammalian Cell Senescence-Sustenance of Muscle Larvae of Trichinella spp.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Nov 28;2022:1799839. doi: 10.1155/2022/1799839. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36478989 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin Preparation from Frozen Tissues for Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assays.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2930:203-217. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4558-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40402456
-
Multifaceted roles of trained immunity in diverse pathological contexts.BMB Rep. 2024 Oct;57(10):431-440. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2024-0045. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 38835118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Netea MG, Quintin J, van der Meer JW. Trained immunity: a memory for innate host defense. Cell Host Microbe 2011;9:355–61. - PubMed
-
- Essers MA, Offner S, Blanco-Bose WE, Waibler Z, Kalinke U, Duchosal MA, et al. . IFNalpha activates dormant haematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Nature 2009;458:904–8. - PubMed
-
- Sato T, Onai N, Yoshihara H, Arai F, Suda T, Ohteki T. Interferon regulatory factor-2 protects quiescent hematopoietic stem cells from type I interferon-dependent exhaustion. Nat Med 2009;15:696–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

