Single-Dose Liposomal Amphotericin B Treatment for Cryptococcal Meningitis
- PMID: 35320642
- PMCID: PMC7612678
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2111904
Single-Dose Liposomal Amphotericin B Treatment for Cryptococcal Meningitis
Abstract
Background: Cryptococcal meningitis is a leading cause of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-related death in sub-Saharan Africa. Whether a treatment regimen that includes a single high dose of liposomal amphotericin B would be efficacious is not known.
Methods: In this phase 3 randomized, controlled, noninferiority trial conducted in five African countries, we assigned HIV-positive adults with cryptococcal meningitis in a 1:1 ratio to receive either a single high dose of liposomal amphotericin B (10 mg per kilogram of body weight) on day 1 plus 14 days of flucytosine (100 mg per kilogram per day) and fluconazole (1200 mg per day) or the current World Health Organization-recommended treatment, which includes amphotericin B deoxycholate (1 mg per kilogram per day) plus flucytosine (100 mg per kilogram per day) for 7 days, followed by fluconazole (1200 mg per day) for 7 days (control). The primary end point was death from any cause at 10 weeks; the trial was powered to show noninferiority at a 10-percentage-point margin.
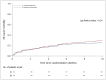
Results: A total of 844 participants underwent randomization; 814 were included in the intention-to-treat population. At 10 weeks, deaths were reported in 101 participants (24.8%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 20.7 to 29.3) in the liposomal amphotericin B group and 117 (28.7%; 95% CI, 24.4 to 33.4) in the control group (difference, -3.9 percentage points); the upper boundary of the one-sided 95% confidence interval was 1.2 percentage points (within the noninferiority margin; P<0.001 for noninferiority). Fungal clearance from cerebrospinal fluid was -0.40 log10 colony-forming units (CFU) per milliliter per day in the liposomal amphotericin B group and -0.42 log10 CFU per milliliter per day in the control group. Fewer participants had grade 3 or 4 adverse events in the liposomal amphotericin B group than in the control group (50.0% vs. 62.3%).
Conclusions: Single-dose liposomal amphotericin B combined with flucytosine and fluconazole was noninferior to the WHO-recommended treatment for HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis and was associated with fewer adverse events. (Funded by the European and Developing Countries Clinical Trials Partnership and others; Ambition ISRCTN number, ISRCTN72509687.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Toward Simpler, Safer Treatment of Cryptococcal Meningitis.N Engl J Med. 2022 Mar 24;386(12):1179-1181. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2201150. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 35320648 No abstract available.
-
Single-Dose Amphotericin B for Cryptococcal Meningitis.N Engl J Med. 2022 Jul 28;387(4):380-381. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2206274. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 35939591 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 098316/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 203135/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 211360/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 NS086312/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 206007/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G1001760/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P020526/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/V033417/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P006922/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_MR/P006922/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- RP-2017-08-ST2-012/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MR/N023005/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 214321/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- K01 TW010268/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
