Safety and Efficacy of a Third Dose of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine
- PMID: 35320659
- PMCID: PMC9006787
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2200674
Safety and Efficacy of a Third Dose of BNT162b2 Covid-19 Vaccine
Abstract
Background: Active immunization with the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech) has been a critical mitigation tool against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection during the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic. In light of reports of waning protection occurring 6 months after the primary two-dose vaccine series, data are needed on the safety and efficacy of offering a third (booster) dose in persons 16 years of age or older.
Methods: In this ongoing, placebo-controlled, randomized, phase 3 trial, we assigned participants who had received two 30-μg doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine at least 6 months earlier to be injected with a third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine or with placebo. We assessed vaccine safety and efficacy against Covid-19 starting 7 days after the third dose.
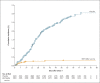
Results: A total of 5081 participants received a third BNT162b2 dose and 5044 received placebo. The median interval between dose 2 and dose 3 was 10.8 months in the vaccine group and 10.7 months in the placebo group; the median follow-up was 2.5 months. Local and systemic reactogenicity events from the third dose were generally of low grade. No new safety signals were identified, and no cases of myocarditis or pericarditis were reported. Among the participants without evidence of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection who could be evaluated, Covid-19 with onset at least 7 days after dose 3 was observed in 6 participants in the vaccine group and in 123 participants in the placebo group, which corresponded to a relative vaccine efficacy of 95.3% (95% confidence interval, 89.5 to 98.3).
Conclusions: A third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine administered a median of 10.8 months after the second dose provided 95.3% efficacy against Covid-19 as compared with two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine during a median follow-up of 2.5 months. (Funded by BioNTech and Pfizer; C4591031 ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04955626.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Statement on the ninth meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee regarding the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. October 26, 2021. (https://www.who.int/news/item/26-10-2021-statement-on-the-ninth-meeting-...).
-
- Sahin U, Muik A, Vogler I, et al. BNT162b2 vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies and poly-specific T cells in humans. Nature 2021;595:572-577. - PubMed
-
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first COVID-19 vaccine. August 23, 2021. (https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-c...).
-
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA authorizes Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine for emergency use in children 5 through 11 years of age. October 29, 2021. (https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-authorizes-pfize...).
-
- McGill COVID19 Vaccine Tracker Team. Pfizer/BioNTech: comirnaty (https://covid19.trackvaccines.org/vaccines/6/).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
