Mobile origin-licensing factors confer resistance to conflicts with RNA polymerase
- PMID: 35320708
- PMCID: PMC8961423
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110531
Mobile origin-licensing factors confer resistance to conflicts with RNA polymerase
Abstract
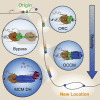
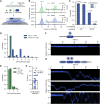
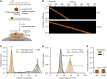
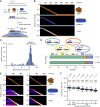
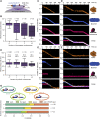
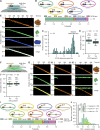
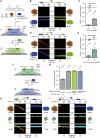
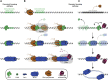
Fundamental to our understanding of chromosome duplication is the idea that replication origins function both as sites where MCM helicases are loaded during the G1 phase and where synthesis begins in S phase. However, the temporal delay between phases exposes the replisome assembly pathway to potential disruption prior to replication. Using multicolor, single-molecule imaging, we systematically study the consequences of encounters between actively transcribing RNA polymerases (RNAPs) and replication initiation intermediates in the context of chromatin. We demonstrate that RNAP can push multiple licensed MCM helicases over long distances with nucleosomes ejected or displaced. Unexpectedly, we observe that MCM helicase loading intermediates also can be repositioned by RNAP and continue origin licensing after encounters with RNAP, providing a web of alternative origin specification pathways. Taken together, our observations reveal a surprising mobility in origin-licensing factors that confers resistance to the complex challenges posed by diverse obstacles encountered on chromosomes.
Keywords: CP; CP: Molecular biology; DNA replication; MCM2-7; Molecular biology; ORC; RNA polymerase; TIRF; chromatin; origin licensing; single molecule; transcription.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bleichert F., Botchan M.R., Berger J.M. Mechanisms for initiating cellular DNA replication. Science. 2017;355:eaah6317. - PubMed
-
- Bramhill D., Kornberg A. Duplex opening by dnaA protein at novel sequences in initiation of replication at the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1988;52:743–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

