A 3D transcriptomics atlas of the mouse nose sheds light on the anatomical logic of smell
- PMID: 35320714
- PMCID: PMC8995392
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110547
A 3D transcriptomics atlas of the mouse nose sheds light on the anatomical logic of smell
Abstract
The sense of smell helps us navigate the environment, but its molecular architecture and underlying logic remain understudied. The spatial location of odorant receptor genes (Olfrs) in the nose is thought to be independent of the structural diversity of the odorants they detect. Using spatial transcriptomics, we create a genome-wide 3D atlas of the mouse olfactory mucosa (OM). Topographic maps of genes differentially expressed in space reveal that both Olfrs and non-Olfrs are distributed in a continuous and overlapping fashion over at least five broad zones in the OM. The spatial locations of Olfrs correlate with the mucus solubility of the odorants they recognize, providing direct evidence for the chromatographic theory of olfaction. This resource resolves the molecular architecture of the mouse OM and will inform future studies on mechanisms underlying Olfr gene choice, axonal pathfinding, patterning of the nervous system, and basic logic for the peripheral representation of smell.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; RNA-seq; machine learning; odorant; olfaction; olfactory epithelium; olfactory mucosa; spatial transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
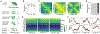
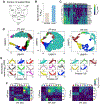
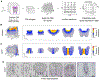

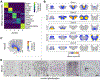
References
-
- Achim K, Pettit J-B, Saraiva LR, Gavriouchkina D, Larsson T, Arendt D, and Marioni JC (2015). High-throughput spatial mapping of single-cell RNA-seq data to tissue of origin. Nat. Biotechnol 33, 503–509. - PubMed
-
- Aldinucci M, Bagnasco S, Lusso S, Pasteris P, Rabellino S, and Vallero S (2017). OCCAM: a flexible, multi-purpose and extendable HPC cluster. J. Phys. Conf. Ser 898, 082039.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

