The Capsule of Acinetobacter baumannii Protects against the Innate Immune Response
- PMID: 35320810
- PMCID: PMC9485954
- DOI: 10.1159/000522232
The Capsule of Acinetobacter baumannii Protects against the Innate Immune Response
Abstract
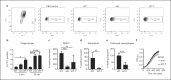
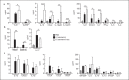
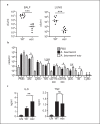
Acinetobacter baumannii is an opportunistic pathogen that has recently emerged as a global threat associated with high morbidity, mortality, and antibiotic resistance. We determined the role of type I interferon (IFN) signaling in A. baumannii infection. We report that A. baumannii can induce a type I IFN response that is dependent upon TLR4-TRIF-IRF3 and phagocytosis of the bacterium. Phase variants of A. baumannii that have a reduced capsule, lead to enhanced TLR4-dependent type I IFN induction. This was also observed in a capsule-deficient strain. However, we did not observe a role for this pathway in vivo. The enhanced signaling could be accounted for by increased phagocytosis in capsule-deficient strains that also lead to enhanced host cell-mediated killing. The increased cytokine response in the absence of the capsule was not exclusive to type I IFN signaling. Several cytokines, including the proinflammatory IL-6, were increased in cells stimulated with the capsule-deficient strain, also observed in vivo. After 4 h in our acute pneumonia model, the burden of a capsule-null strain was significantly reduced, yet we observed increases in innate immune cells and inflammatory markers compared to wild-type A. baumannii. This study underscores the role of phase variation in the modulation of host immune responses and indicates that the capsule of A. baumannii plays an important role in protection against host cell killing and evasion from activation of the innate immune response.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Capsule; Host-pathogen interactions; Innate response; Lung; Pneumonia; Type I interferon; Type III interferon.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Antunes LC, Visca P, Towner KJ. Acinetobacter baumannii: evolution of a global pathogen. Pathog Dis. 2014;71((3)):292–301. - PubMed
-
- Dijkshoorn L, Nemec A, Seifert H. An increasing threat in hospitals: multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5((12)):939–51. - PubMed
-
- Dexter C, Murray GL, Paulsen IT, Peleg AY. Community-acquired Acinetobacter baumannii: clinical characteristics, epidemiology and pathogenesis. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2015;13((5)):567–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

