Aorta in Pathologies May Function as an Immune Organ by Upregulating Secretomes for Immune and Vascular Cell Activation, Differentiation and Trans-Differentiation-Early Secretomes may Serve as Drivers for Trained Immunity
- PMID: 35320939
- PMCID: PMC8934864
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.858256
Aorta in Pathologies May Function as an Immune Organ by Upregulating Secretomes for Immune and Vascular Cell Activation, Differentiation and Trans-Differentiation-Early Secretomes may Serve as Drivers for Trained Immunity
Abstract
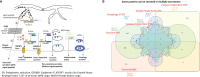
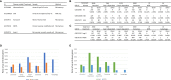
To determine whether aorta becomes immune organ in pathologies, we performed transcriptomic analyses of six types of secretomic genes (SGs) in aorta and vascular cells and made the following findings: 1) 53.7% out of 21,306 human protein genes are classified into six secretomes, namely, canonical, caspase 1, caspase 4, exosome, Weibel-Palade body, and autophagy; 2) Atherosclerosis (AS), chronic kidney disease (CKD) and abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) modulate six secretomes in aortas; and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV, COVID-19 homologous) infected endothelial cells (ECs) and angiotensin-II (Ang-II) treated vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) modulate six secretomes; 3) AS aortas upregulate T and B cell immune SGs; CKD aortas upregulate SGs for cardiac hypertrophy, and hepatic fibrosis; and AAA aorta upregulate SGs for neuromuscular signaling and protein catabolism; 4) Ang-II induced AAA, canonical, caspase 4, and exosome SGs have two expression peaks of high (day 7)-low (day 14)-high (day 28) patterns; 5) Elastase induced AAA aortas have more inflammatory/immune pathways than that of Ang-II induced AAA aortas; 6) Most disease-upregulated cytokines in aorta may be secreted via canonical and exosome secretomes; 7) Canonical and caspase 1 SGs play roles at early MERS-CoV infected ECs whereas caspase 4 and exosome SGs play roles in late/chronic phases; and the early upregulated canonical and caspase 1 SGs may function as drivers for trained immunity (innate immune memory); 8) Venous ECs from arteriovenous fistula (AVF) upregulate SGs in five secretomes; and 9) Increased some of 101 trained immunity genes and decreased trained tolerance regulator IRG1 participate in upregulations of SGs in atherosclerotic, Ang-II induced AAA and CKD aortas, and MERS-CoV infected ECs, but less in SGs upregulated in AVF ECs. IL-1 family cytokines, HIF1α, SET7 and mTOR, ROS regulators NRF2 and NOX2 partially regulate trained immunity genes; and NRF2 plays roles in downregulating SGs more than that of NOX2 in upregulating SGs. These results provide novel insights on the roles of aorta as immune organ in upregulating secretomes and driving immune and vascular cell differentiations in COVID-19, cardiovascular diseases, inflammations, transplantations, autoimmune diseases and cancers.
Keywords: DAMPs; canonical and noncanonical secretomes; coronavirus infection; endothelial cell; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Sun, Xu, Saaoud, Shao, Drummer, Wu, Hu, Yu, Kunapuli, Bethea, Vazquez-Padron, Sun, Jiang, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

