MicroRNA-194-5p Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Targeting P21-Activated Kinase 2
- PMID: 35321102
- PMCID: PMC8934884
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.815916
MicroRNA-194-5p Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Targeting P21-Activated Kinase 2
Abstract
Objective: Many studies have reported that microRNAs (miRs) are involved in the regulation of doxorubicin (DOX)-induced cardiotoxicity. MiR-194-5p has been reported significantly upregulated in patients with myocardial infarction; however, its role in myocardial diseases is still unclear. Various stimuluses can trigger the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and it may activate the apoptosis signals eventually. This study aims to explore the regulatory role of miR-194-5p in DOX-induced ER stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Methods: H9c2 was treated with 2 μM DOX to induce apoptosis, which is to stimulate the DOX-induced cardiotoxicity model. The expression of miR-194-5p was detected by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR); the interaction between miR-194-5p and P21-activated kinase 2 (PAK2) was tested by dual luciferase reporter assay; terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assay and caspase-3/7 activity were used to assess apoptosis; trypan blue staining was applied to measure cell death; Western blotting was performed to detect protein expressions; and ER-related factors splicing X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1s) was detected by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunofluorescence to verify the activation of ER stress.
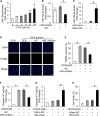
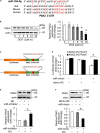
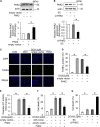
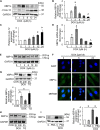
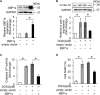
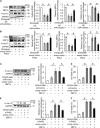
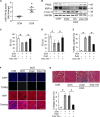
Results: MiR-194-5p was upregulated in cardiomyocytes and mouse heart tissue with DOX treatment, while the protein level of PAK2 was downregulated. PAK2 was predicted as the target of miR-194-5p; hence, dual luciferase reporter assay indicated that miR-194-5p directly interacted with PAK2 and inhibited its expression. TUNEL assay, caspase-3/7 activity test, and trypan blue stain results showed that either inhibition of miR-194-5p or overexpression of PAK2 reduced DOX-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Silencing of miR-194-5p also improved DOX-induced cardiac dysfunction. In addition, DOX could induce ER stress in H9c2, which led to XBP1 and caspase-12 activation. The expression level of XBP1s with DOX treatment increased first then decreased. Overexpression of XBP1s suppressed DOX-induced caspase-3/7 activity elevation as well as the expression of cleaved caspase-12, which protected cardiomyocyte from apoptosis. Additionally, the activation of XBP1s was regulated by miR-194-5p and PAK2.
Conclusion: Our findings revealed that silencing miR-194-5p could alleviate DOX-induced cardiotoxicity via PAK2 and XBP1s in vitro and in vivo. Thus, the novel miR-194-5p/PAK2/XBP1s axis might be the potential prevention/treatment targets for cancer patients receiving DOX treatment.
Keywords: ER stress; apoptosis; cardiotoxicity; doxorubicin; miR-194-5p.
Copyright © 2022 Fa, Xiao, Chang, Ding, Yang, Wang, Wang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA miR-215-5p Regulates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiomyocyte Injury by Targeting ZEB2.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 1;78(4):622-629. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001110. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34282068
-
MicroRNA-31-5p attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via quaking and circular RNA Pan3.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020 Mar;140:56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.02.009. Epub 2020 Mar 3. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32135167
-
MiR-15b-5p is Involved in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Inhibiting Bmpr1a Signal in H9c2 Cardiomyocyte.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019 Jun;19(3):264-275. doi: 10.1007/s12012-018-9495-6. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30535663
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Doxorubicin-Induced Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 12;25(24):13335. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413335. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity-an update.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 12;15:1415108. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1415108. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39188945 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Panax notoginseng Saponins Alleviate Coronary Artery Disease Through Hypermethylation of the miR-194-MAPK Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 16;13:829416. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.829416. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35784716 Free PMC article.
-
Sinapic Acid Ameliorates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress Through Activation of the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 13;14(3):337. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030337. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227457 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-194-5p avoids DUSP9 downregulation thus limiting sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 2;14(1):20313. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71166-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39218968 Free PMC article.
-
Sprouty-related proteins with EVH1 domain (SPRED2) prevents high-glucose induced endothelial-mesenchymal transition and endothelial injury by suppressing MAPK activation.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13882-13892. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2086351. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35707829 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming Cardiotoxicity Detection in Cancer Therapies: The Promise of MicroRNAs as Precision Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 6;25(22):11910. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211910. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39595980 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Davies KJ, Doroshow JH. Redox cycling of anthracyclines by cardiac mitochondria. I. Anthracycline radical formation by NADH dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. (1986) 261:3060–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

