Iron overload status in patients with non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia in China
- PMID: 35321211
- PMCID: PMC8935562
- DOI: 10.1177/20406207221084639
Iron overload status in patients with non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia in China
Abstract
Background: Iron overload is one of the main factors that increase morbidity and mortality in patients with non-transfusion dependent thalassemia (NTDT).
Aim: This study aimed at investigating the prevalence and severity of iron overload in Chinese NTDT patients.
Methods: we analyzed serum ferritin (SF), liver iron concentration (LIC) and cardiac T2* in 178 Chinese NTDT in this cross-sectional study.
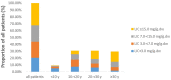
Results: The median SF level was 996.00(27.15-19704.00) ng/ml and the median LIC value was 8.90(0.60-43.00) mg Fe/g dry weight (dw). The youngest patient with liver iron overload was 5 years old with 5.6 mg Fe/g dw in LIC. The median cardiac T2* was 33.06(7.46-75.08) ms. 6 patients had cardiac T2*⩽20ms. The patients with β thalassemia intermedia and HbE/β thalassemia showed a statistically significant lower Hb and higher values of SF and LIC than those of hemoglobin H disease patients. On multivariate logistic regression analysis, patients in ⩾ age 30-year old had a significant higher risk for iron overload (OR: 77.75, 95% CI: 8.76-690.49) in the age group. The detailed analysis of proportions of different LIC indicate in > 30-year old group, 76.8% patients suffered from moderate and severe LIC.
Conclusion: Our study provides a strong support for the novel findings that Chinese NTDT patients have a high prevalence of iron overload. The first assessment of MRI LIC should be performed as early as 5 years old. Then, NTDT patients > 30 years old may suffer with a high burden of iron overload.
Keywords: Chinese thalassemic patients; iron overload; non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation of Serum Ferritin and Liver Iron Concentration with Transient Liver Elastography in Adult Thalassemia Intermedia Patients with Blood Transfusion.J Blood Med. 2021 Apr 15;12:235-243. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S303703. eCollection 2021. J Blood Med. 2021. PMID: 33883962 Free PMC article.
-
Iron overload in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia: association with genotype and clinical risk factors.Int J Hematol. 2016 Jun;103(6):643-8. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-1991-5. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Int J Hematol. 2016. PMID: 27052211
-
Deferasirox effectively reduces iron overload in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT) patients: 1-year extension results from the THALASSA study.Ann Hematol. 2013 Nov;92(11):1485-93. doi: 10.1007/s00277-013-1808-z. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Ann Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23775581 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Thalassemia Intermedia: Chelator or Not?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 5;23(17):10189. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710189. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iron overload in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia: a clinical perspective.Blood Rev. 2012 Apr;26 Suppl 1:S16-9. doi: 10.1016/S0268-960X(12)70006-1. Blood Rev. 2012. PMID: 22631036 Review.
Cited by
-
[Consensus of experts on diagnosis and treatment of non-transfusion dependent thalassemia in China(2018 edition)].Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Sep 14;39(9):705-708. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2018.09.001. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30369178 Free PMC article. Chinese. No abstract available.
-
Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of Tissue Iron Deposition and Cardiac Function in Adult Regularly Transfused Thalassemia Intermedia Compared with Thalassemia Major Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 14;13(16):4791. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164791. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200932 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Mullerian Hormone Evaluates Ovarian Function in Patients with Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2025 Jan 1;17(1):e2025007. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2025.007. eCollection 2025. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39830793 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Relationship Between Non-Transferrin-Bound Iron (NTBI), Labile Plasma Iron (LPI), and Iron Toxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 3;26(13):6433. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136433. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia: A Panoramic Review.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Oct 21;58(10):1496. doi: 10.3390/medicina58101496. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36295656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Weatherall DJ. The definition and epidemiology of non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia. Blood Rev 2012; 26(Suppl. 1): S3–S6. - PubMed
-
- Musallam KM, Cappellini MD, Wood JC, et al.. Iron overload in non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia: a clinical perspective. Blood Rev 2012; 26(Suppl. 1): S16–S19. - PubMed
-
- Musallam KM, Motta I, Salvatori M, et al.. Longitudinal changes in serum ferritin levels correlate with measures of hepatic stiffness in transfusion-independent patients with beta-thalassemia intermedia. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2012; 49: 136–139. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

