Detailed analyses of microstructure of photoreceptor layer at different severities of occult macular dystrophy by ultrahigh-resolution SD-OCT
- PMID: 35321252
- PMCID: PMC8935511
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajoc.2022.101490
Detailed analyses of microstructure of photoreceptor layer at different severities of occult macular dystrophy by ultrahigh-resolution SD-OCT
Abstract
Purpose: To analyze the microstructures of the photoreceptor layer in detail in eyes with occult macular dystrophy (OMD, Miyake's disease) by ultrahigh-resolution spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (UHR-SD-OCT).
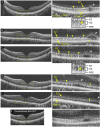
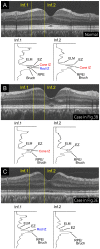
Observations: Twenty-eight normal subjects and 5 patients with OMD of different severities were studied. Cross-sectional images through the fovea were recorded with a UHR-SD-OCT system with a depth resolution of <2.0 μm. In patients with OMD, the UHR-SD-OCT images revealed abnormal photoreceptor microstructures which were not detected in the conventional SD-OCT images. The UHR-SD-OCT images showed that the interdigitation zone (IZ) was not present and the outer segments were hyperreflective with hyperreflective dots (HRDs) aligned like string of pearls during the earlier stages. There was a disruption of the ellipsoid zone (EZ) which appeared as clusters of larger HRDs, and these HRDs became less apparent with increasing time. The outer segments became hyporeflective and rod IZ became apparent with longer duration of the disease process.
Conclusions and importance: The UHR-SD-OCT images show detailed characteristics of the photoreceptor microstructures of different severities during the progression of OMD. These detailed observations will help in understanding the mechanisms involved in the retinal pathology and should provide important information for their treatments.
Keywords: Ellipsoid zone; Interdigitation zone; Occult macular dystrophy; Optical coherence tomography; Photoreceptors; Ultrahigh-resolution OCT.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
K.T.: Payment for lectures - Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma Co., Ltd., Kowa Company, Ltd., and Senju Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Receipt of equipment - Kowa Company, Ltd. G.H.: None. The funding sources had no role in the design and conduct of this study; collection, management, analysis, interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. We thank all the subjects for participation in this study. We thank Masaharu Mizouchi of Kowa Company for technical support. We thank our collaborators, Takeshi Iwata and Kaoru Fujinami of the National Institute of Sensory Organs for their contributions in genetic analysis of the patients. We also thank Professor Emeritus Duco Hamasaki of the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami School of Medicine, Miami, FL for editing our manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Drexler W., Fujimoto J.G. State-of-the-art retinal optical coherence tomography. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2008;27:45–88. - PubMed
-
- Miyake Y., Ichikawa K., Shiose Y., Kawase Y. Hereditary macular dystrophy without visible fundus abnormality. Am J Ophthalmol. 1989;108:292–299. - PubMed
-
- Miyake Y., Horiguchi M., Tomita N., et al. Occult macular dystrophy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996;122:644–653. - PubMed
-
- Tsunoda K., Usui T., Hatase T., et al. Clinical characteristics of occult macular dystrophy in family with mutation of Rp1l1 gene. Retina-the J. Retin. Vit. Dis. 2012;32:1135–1147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

