Influence of probenecid on endoxifen systemic exposure in breast cancer patients on adjuvant tamoxifen treatment
- PMID: 35321309
- PMCID: PMC8935557
- DOI: 10.1177/17588359221081075
Influence of probenecid on endoxifen systemic exposure in breast cancer patients on adjuvant tamoxifen treatment
Abstract
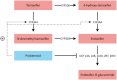
Introduction: In breast cancer patients treated with the anti-estrogen tamoxifen, low concentrations of the active metabolite endoxifen are associated with more disease recurrence. We hypothesized that we could increase endoxifen concentrations by induction of its formation and inhibition of its metabolism by co-administration of probenecid.
Methods: We conducted a crossover study and measured endoxifen concentrations in patients on steady-state tamoxifen monotherapy and after 14 days of combination treatment with probenecid. Eleven evaluable patients were included.
Results: Treatment with tamoxifen and probenecid resulted in a 26% increase of endoxifen area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 to 24 h (AUC0-24h) compared to tamoxifen monotherapy (95% confidence interval [CI]: 8-46%; p < 0.01), while the maximum observed endoxifen concentration increased with 24% (95% CI: 7-44%; p < 0.01). The metabolic ratio of endoxifen to tamoxifen increased with 110% (95% CI: 82-143%; p < 0.001) after the addition of probenecid.
Conclusion: Probenecid resulted in a clinically relevant increase of endoxifen concentrations in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant tamoxifen. This combination therapy could provide a solution for patients with a CYP2D6-poor metabolizer phenotype or endoxifen concentrations below the threshold despite earlier tamoxifen dose.
Keywords: breast cancer; endoxifen; metabolism; probenecid; tamoxifen.
© The Author(s), 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adjusting the dose of tamoxifen in patients with early breast cancer and CYP2D6 poor metabolizer phenotype.Breast. 2014 Aug;23(4):400-6. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2014.02.008. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Breast. 2014. PMID: 24685597
-
Limited predictive value of achieving beneficial plasma (Z)-endoxifen threshold level by CYP2D6 genotyping in tamoxifen-treated Polish women with breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2015 Aug 1;15:570. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1575-4. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26232141 Free PMC article.
-
The use of the 13C-dextromethorphan breath test for phenotyping CYP2D6 in breast cancer patients using tamoxifen: association with CYP2D6 genotype and serum endoxifen levels.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;71(3):593-601. doi: 10.1007/s00280-012-2034-4. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23228987
-
Generating a Precision Endoxifen Prediction Algorithm to Advance Personalized Tamoxifen Treatment in Patients with Breast Cancer.J Pers Med. 2021 Mar 13;11(3):201. doi: 10.3390/jpm11030201. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33805613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical CYP2D6 Genotyping to Personalize Adjuvant Tamoxifen Treatment in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Patients: Current Status of a Controversy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 12;13(4):771. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040771. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33673305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics of Tamoxifen and Its Major Metabolites and the Effect of the African Ancestry Specific CYP2D6*17 Variant on the Formation of the Active Metabolite, Endoxifen.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 31;13(2):272. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020272. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836506 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

