Health, Human Capital and Domestic Violence
- PMID: 35321345
- PMCID: PMC8939878
- DOI: 10.3368/jhr.56.4.1115-7543r5
Health, Human Capital and Domestic Violence
Abstract
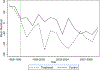
We treat health as a form of human capital and hypothesize that women with more human capital face stronger incentives to make costly investments with future payoffs, such as avoiding abusive partners and reducing drug use. To test this hypothesis, we exploit the unanticipated introduction of an HIV treatment, HAART, which dramatically improved HIV+ women's health. We find that after the introduction of HAART HIV+ women who experienced increases in expected longevity exhibited a decrease in domestic violence of 15% and in drug use of 1520%. We rule out confounding via secular trends using a control group of healthier women.
Keywords: Domestic Violence; Drug Use; HIV/AIDS; Health; Human Capital; I1; J12; J24; Medical Innovation; O39; Risky Behavior.
Figures


References
-
- AIDSinfo. 2014. “Guidelines for the Use of Antiretroviral Agents in HIV-1-Infected Adults and Adolescents,” http://aidsinfo.nih.gov/guidelines.
-
- Anderberg Dan and Rainer Helmut. 2013. “Economic Abuse: A Theory of Intrahousehold Sabotage,” Journal of Public Economics, 97(01–13): 282–295.
-
- Angelucci Manuela. 2008. “Love on the Rocks: Domestic Violence and Alcohol Abuse in Rural Mexico,” The BE Journal of Economic Analysis & Policy, 8 (1): 1935–1682.
Grants and funding
- U01 AI103397/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI031834/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI035004/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034989/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034994/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103401/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL146202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000004/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103408/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI103390/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034993/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD032632/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI042590/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
