Molecular targets of statins and their potential side effects: Not all the glitter is gold
- PMID: 35321818
- PMCID: PMC9007885
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.174906
Molecular targets of statins and their potential side effects: Not all the glitter is gold
Abstract
Statins are a class of drugs widely used worldwide to manage hypercholesterolemia and the prevention of secondary heart attacks. Currently, available statins vary in terms of their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. Although the primary target of statins is the inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR), the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis, statins exhibit many pleiotropic effects downstream of the mevalonate pathway. These pleiotropic effects include the ability to reduce myocardial fibrosis, pathologic cardiac disease states, hypertension, promote bone differentiation, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor effects through multiple mechanisms. Although these pleiotropic effects of statins may be a cause for enthusiasm, there are many adverse effects that, for the most part, are unappreciated and need to be highlighted. These adverse effects include myopathy, new-onset type 2 diabetes, renal and hepatic dysfunction. Although these adverse effects may be relatively uncommon, considering the number of people worldwide who use statins daily, the actual number of people affected becomes quite large. Also, co-administration of statins with several other medications, herbal agents, and foods, which interact through common enzymatic pathways, can have untoward clinical consequences. In this review, we address these concerns.
Keywords: Diabetes; Drug interactions; Myopathy; Pleiotropy; Statins.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
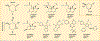
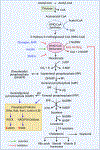
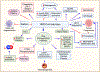
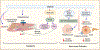
References
-
- Agarwal R, 2004. Statin Induced Proteinuria: Renal Injury or Renoprotection? Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 15, 2502. - PubMed
-
- Ahmadi Y, Ghorbanihaghjo A, Argani H, 2017. The balance between induction and inhibition of mevalonate pathway regulates cancer suppression by statins: A review of molecular mechanisms. Chem Biol Interact 273, 273–285. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa M, Rabkin E, Sugiyama S, Voglic SJ, Fukumoto Y, Furukawa Y, Shiomi M, Schoen FJ, Libby P, 2001. An HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor, Cerivastatin, Suppresses Growth of Macrophages Expressing Matrix Metalloproteinases and Tissue Factor In Vivo and In Vitro. Circulation 103, 276–283. - PubMed
-
- Altaf A, Qu P, Zhao Y, Wang H, Lou D, Niu N, 2015. NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood monocytes of acute coronary syndrome patients and its relationship with statins. Coronary Artery Disease 26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

