Advances in COVID-19 mRNA vaccine development
- PMID: 35322018
- PMCID: PMC8940982
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-022-00950-y
Advances in COVID-19 mRNA vaccine development
Abstract
To date, the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has determined 399,600,607 cases and 5,757,562 deaths worldwide. COVID-19 is a serious threat to human health globally. The World Health Organization (WHO) has declared COVID-19 pandemic a major public health emergency. Vaccination is the most effective and economical intervention for controlling the spread of epidemics, and consequently saving lives and protecting the health of the population. Various techniques have been employed in the development of COVID-19 vaccines. Among these, the COVID-19 messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccine has been drawing increasing attention owing to its great application prospects and advantages, which include short development cycle, easy industrialization, simple production process, flexibility to respond to new variants, and the capacity to induce better immune response. This review summarizes current knowledge on the structural characteristics, antigen design strategies, delivery systems, industrialization potential, quality control, latest clinical trials and real-world data of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines as well as mRNA technology. Current challenges and future directions in the development of preventive mRNA vaccines for major infectious diseases are also discussed.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
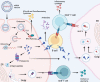
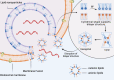
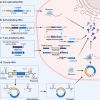
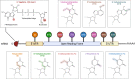
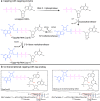


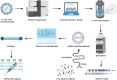
References
-
- Zhang J-j, et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. ALLERGY. 2020;75:1730–1741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

