COVID-19, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation in the Depression Route
- PMID: 35322375
- PMCID: PMC8942178
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-022-02004-y
COVID-19, Oxidative Stress, and Neuroinflammation in the Depression Route
Abstract
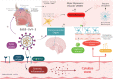
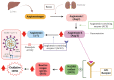
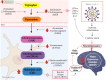
COVID-19 is associated with oxidative stress, peripheral hyper inflammation, and neuroinflammation, especially in individuals with a more severe form of the disease. Some studies provide evidence on the onset or exacerbation of major depressive disorder (MDD), among other psychiatric disorders due to COVID-19. Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation are associated conditions, especially in the more severe form of MDD and in refractoriness to available therapeutic strategies. Inflammatory cytokines in the COVID-19 hyper inflammation process can activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) enzyme. IDO activation can reduce tryptophan and increase toxic metabolites of the kynurenine pathway, which increases glial activation, neuroinflammation, toxicity, and neuronal death. This review surveyed a number of studies and analyzed the mechanisms of oxidative stress, inflammation, and neuroinflammation involved in COVID-19 and depression. Finally, the importance of more protocols that can help elucidate the interaction between these mechanisms underlying COVID-19 and MDD and the possible therapeutic strategies involved in the interaction of these mechanisms are highlighted.
Keywords: COVID-19; Glial activation; Major depressive disorder; Neuroinflammation; Oxidative stress.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed AU. An overview of inflammation: mechanism and consequences. Front Biol (beijing) 2011;6:274. doi: 10.1007/s11515-011-1123-9. - DOI
-
- Alamdari DH, Moghaddam AB, Amini S, Keramati MR, Zarmehri AM, Alamdari AH, Damsaz M, Banpour H, Yarahmadi A, Koliakos G. Application of methylene blue -vitamin C –N-acetyl cysteine for treatment of critically ill COVID-19 patients, report of a phase-I clinical trial. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173494. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani AS, Mukhtar N, Aljomaiah A, Aljamei H, Bakhsh A, Alsudani N, Elsayed T, Alrashidi N, Fadel R, Alqahtani E, Raef H, Butt MI, Sulaiman O. The impact of COVID-19 viral infection on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Endocr Pract. 2021;27:83–89. doi: 10.1016/j.eprac.2020.10.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

