Extracellular vesicles-associated tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs): biogenesis, biological functions, and their role as potential biomarkers in human diseases
- PMID: 35322869
- PMCID: PMC9110440
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-022-02189-0
Extracellular vesicles-associated tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs): biogenesis, biological functions, and their role as potential biomarkers in human diseases
Abstract
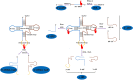
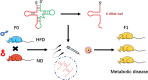
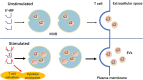
Traditionally, transfer RNAs (tRNAs) specifically decoded messenger RNA (mRNA) and participated in protein translation. tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs), also known as tRNA-derived small RNAs (tsRNAs), are generated by the specific cleavage of pre- and mature tRNAs and are a class of newly defined functional small non-coding RNAs (sncRNAs). Following the different cleavage positions of precursor or mature tRNA, tRFs are classified into seven types, 5'-tRNA half, 3'-tRNA half, tRF-1, 5'U-tRF, 3'-tRF, 5'-tRF, and i-tRF. It has been demonstrated that tRFs have a diverse range of biological functions in cellular processes, which include inhibiting protein translation, modulating stress response, regulating gene expression, and involvement in cell cycles and epigenetic inheritance. Emerging evidences have indicated that tRFs in extracellular vesicles (EVs) seem to act as regulatory molecules in various cellular processes and play essential roles in cell-to-cell communication. Furthermore, the dysregulation of EV-associated tRFs has been associated with the occurrence and progression of a variety of cancers and they can serve as novel potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis. In this review, the biogenesis and classification of tRFs are summarized, and the biological functions of EV-associated tRFs and their roles as potential biomarkers in human diseases are discussed.
Keywords: Biological functions; Biomarker; Cancer; Extracellular vesicles (EVs); tRNA-derived fragments (tRFs).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

