Nomogram for predicting the overall survival of patients with early-onset prostate cancer: A population-based retrospective study
- PMID: 35322943
- PMCID: PMC9468440
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4694
Nomogram for predicting the overall survival of patients with early-onset prostate cancer: A population-based retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The incidence of early-onset prostate cancer (PCa) has increased significantly over the past few decades. It is necessary to develop a prognostic nomogram for the prediction of overall survival (OS) in early-onset PCa patients.
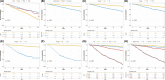
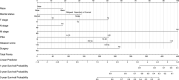
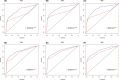
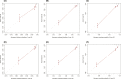
Methods: A total of 23,730 early-onset PCa patients (younger than 55 years old) between 2010 and 2015 in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database were enrolled for the current study, and randomly separated into the training cohort and the validation cohort. 361 eligible early-onset PCa patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas-Prostate Adenocarcinoma (TCGA-PRAD) cohort were obtained as the external validation cohort. Independent predictors were selected by univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis, and a prognostic nomogram was constructed for 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS. The accurate and discriminative abilities of the nomogram were evaluated by the concordance index (C-index), receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC), calibration plot, net reclassification index (NRI), and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI).
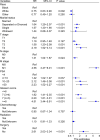
Results: Multivariate Cox analysis showed that race, marital status, TNM stage, prostate-specific antigen, Gleason score, and surgery were significantly associated with poor prognosis of PCa. A nomogram consisting of these variables was established, which had higher C-indexes than the TNM system (training cohort: 0.831 vs. 0.746, validation cohort: 0.817 vs. 0.752). Better AUCs of the nomogram than the TNM system at 1, 3, and 5 years were found in both the training cohort and the validation cohort. The 3-year and 5-year AUCs of the nomogram in the TCGA-PRAD cohort were 0.723 and 0.679, respectively. The calibration diagram, NRI, and IDI also showed promising prognostic value in OS.
Conclusions: We developed an effective prognostic nomogram for OS prediction in early-onset PCa patients, which will further assist both the precise clinical treatment and the assessment of long-term outcomes.
Keywords: early-onset; nomogram; overall survival; prognosis; prostate cancer.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209‐249. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7‐33. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich A, Aus G, Bolla M, et al. EAU guidelines on prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2008;53(1):68‐80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

