An Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Aptasensor for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD Using a Carbon Nanofiber-Gold Nanocomposite Modified Screen-Printed Electrode
- PMID: 35323412
- PMCID: PMC8945915
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12030142
An Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy-Based Aptasensor for the Determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD Using a Carbon Nanofiber-Gold Nanocomposite Modified Screen-Printed Electrode
Abstract
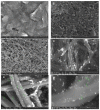
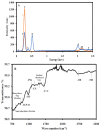
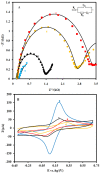
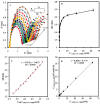
Worldwide, human health is affected by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Hence, the fabrication of the biosensors to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 is critical. In this paper, we report an electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)-based aptasensor for the determination of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (SARS-CoV-2-RBD). For this purpose, the carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were first decorated with gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). Then, the surface of the carbon-based screen-printed electrode (CSPE) was modified with the CNF-AuNP nanocomposite (CSPE/CNF-AuNP). After that, the thiol-terminal aptamer probe was immobilized on the surface of the CSPE/CNF-AuNP. The surface coverage of the aptamer was calculated to be 52.8 pmol·cm-2. The CSPE/CNF-AuNP/Aptamer was then used for the measurement of SARS-CoV-2-RBD by using the EIS method. The obtained results indicate that the signal had a linear-logarithmic relationship in the range of 0.01-64 nM with a limit of detection of 7.0 pM. The proposed aptasensor had a good selectivity to SARS-CoV-2-RBD in the presence of human serum albumin; human immunoglobulins G, A, and M, hemagglutinin, and neuraminidase. The analytical performance of the aptasensor was studied in human saliva samples. The present study indicates a practical application of the CSPE/CNF-AuNP/Aptamer for the determination of SARS-CoV-2-RBD in human saliva samples with high sensitivity and accuracy.
Keywords: CNF–AuNP; SARS-CoV-2-RBD; aptasensor; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Soares J.C., Soares A.C., Rodrigues V.C., Oiticica P.R.A., Raymundo-Pereira P.A., Bott-Neto J.L., Buscaglia L.A., de Castro L.D.C., Ribas L.C., Scabini L., et al. Detection of a SARS-CoV-2 sequence with genosensors using data analysis based on information visualization and machine learning techniques. Mater. Chem. Front. 2021;5:5658–5670. doi: 10.1039/D1QM00665G. - DOI
-
- Seo G., Lee G., Kim M.J., Baek S.-H., Choi M., Ku K.B., Lee C.-S., Jun S., Park D., Kim H.G., et al. Rapid detection of COVID-19 causative virus (SARS-CoV-2) in human nasopharyngeal swab specimens using field-effect transistor-based biosensor. ACS Nano. 2020;14:5135–5142. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02823. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

