Preparation and Characterization of Nano-Selenium Decorated by Chondroitin Sulfate Derived from Shark Cartilage and Investigation on Its Antioxidant Activity
- PMID: 35323471
- PMCID: PMC8951027
- DOI: 10.3390/md20030172
Preparation and Characterization of Nano-Selenium Decorated by Chondroitin Sulfate Derived from Shark Cartilage and Investigation on Its Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
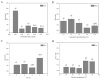
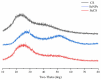
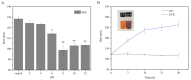
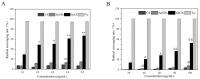
In the present study, a selenium-chondroitin sulfate (SeCS) was synthesized by the sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) and ascorbic acid (Vc) redox reaction using chondroitin sulfate derived from shark cartilage as a template, and characterized by SEM, SEM-EDS, FTIR and XRD. Meanwhile, its stability was investigated at different conditions of pH and temperatures. Besides, its antioxidant activity was further determined by the DPPH and ABTS assays. The results showed the SeCS with the smallest particle size of 131.3 ± 4.4 nm and selenium content of 33.18% was obtained under the optimal condition (CS concentration of 0.1 mg/mL, mass ratio of Na2SeO3 to Vc of 1:8, the reaction time of 3 h, and the reaction temperature of 25 °C). SEM image showed the SeCS was an individual and spherical nanostructure and its structure was evidenced by FTIR and XRD. Meanwhile, SeCS remained stable at an alkaline pH and possessed good storage stability at 4 °C for 28 days. The results on scavenging free radical levels showed that SeCS exhibited significantly higher antioxidant activity than SeNPs and CS, indicating that SeCS had a potential antioxidant effect.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; chondroitin sulfate derived from shark cartilage; nanoselenium; structure characterization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang Y.Y., Qiu Y., Sun L., Ding Z.C., Yan J.K. Preparation, characterization, and antioxidant capacities of selenium nanoparticles stabilized using polysaccharide–protein complexes from Corbicula fluminea. Food Biosci. 2018;26:177–184. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2018.10.014. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 230419100/Guangdong Ocean University Innovation Program
- 2020A1515010860 and 2021A1515012455/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- QNXZ201909/Nanhai Youth Scholar Project of Guangdong Ocean University
- 2020A01034/the Project of Science and Technology of Zhanjiang City
- R17034/the Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Ocean University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

