Rapid Mining of Novel α-Glucosidase and Lipase Inhibitors from Streptomyces sp. HO1518 Using UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS
- PMID: 35323488
- PMCID: PMC8955712
- DOI: 10.3390/md20030189
Rapid Mining of Novel α-Glucosidase and Lipase Inhibitors from Streptomyces sp. HO1518 Using UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS
Abstract
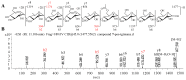
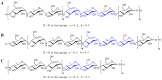
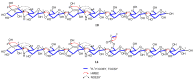
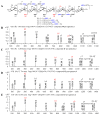
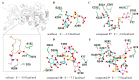
A rapid and sensitive method using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS) was applied for the analysis of the metabolic profile of acarviostatin-containing aminooligosaccharides derived from Streptomyces sp. HO1518. A total of ninety-eight aminooligosaccharides, including eighty potential new compounds, were detected mainly based on the characteristic fragment ions originating from quinovosidic bond cleavages in their molecules. Following an LC-MS-guided separation technique, seven new aminooligosaccharides (10-16) along with four known related compounds (17-20) were obtained directly from the crude extract of strain HO1518. Compounds 10-13 represent the first examples of aminooligosaccharides with a rare acarviostatin II02-type structure. In addition, all isolates displayed considerable inhibitory effects on three digestive enzymes, which revealed that the number of the pseudo-trisaccharide core(s), the feasible length of the oligosaccharides, and acyl side chain exerted a crucial influence on their bioactivities. These results demonstrated that the UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS-based metabolomics approach could be applied for the rapid identification of aminooligosaccharides and other similar structures in complex samples. Furthermore, this study highlights the potential of acylated aminooligosaccharides with conspicuous α-glucosidase and lipase inhibition for the future development of multi-target anti-diabetic drugs.
Keywords: Streptomyces sp. HO1518; UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS; aminooligosaccharides; diabetes; digestive enzyme inhibitors; metabolic profiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
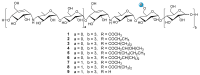

Similar articles
-
Acylated Aminooligosaccharides from the Yellow Sea Streptomyces sp. HO1518 as Both α-Glucosidase and Lipase Inhibitors.Mar Drugs. 2020 Nov 20;18(11):576. doi: 10.3390/md18110576. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 33233702 Free PMC article.
-
Acylated Aminooligosaccharides with Inhibitory Effects against α-Amylase from Streptomyces sp. HO1518.Mar Drugs. 2018 Oct 23;16(11):403. doi: 10.3390/md16110403. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 30360574 Free PMC article.
-
Two novel aminooligosaccharides isolated from the culture of Streptomyces coelicoflavus ZG0656 as potent inhibitors of alpha-amylase.Carbohydr Res. 2008 Feb 25;343(3):470-6. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2007.11.012. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Carbohydr Res. 2008. PMID: 18054350
-
An integrated strategy of ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry and virtual screening for the identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors in acarviostatin-containing complex.J Chromatogr A. 2013 Dec 6;1319:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.10.035. J Chromatogr A. 2013. PMID: 24377104
-
Screening and identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves by ultrafiltration coupled with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and molecular docking.J Chromatogr A. 2022 Jul 19;1675:463160. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463160. Epub 2022 May 19. J Chromatogr A. 2022. PMID: 35635870
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2018YFA0900600/National Key R&D Program of China
- 41876084, 31670099/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- XDB27020202, XDB27020103/Strategic Priority Research Program "Molecular mechanism of Plant Growth and Development" of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- ZSYS-016/Construction of the Registry and Database of Bioparts for Synthetic Biology of Chinese Academy of Sciences
- 20XD1404400/Program of Shanghai Academic Research Leader
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

